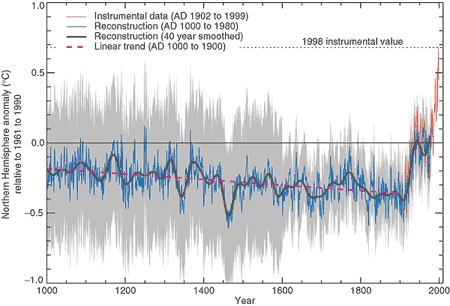
Figure 1: Northern Hemisphere temperature changes estimated from various proxy records shown in blue (Mann et al. 1999). Instrumental data shown in red. Note the large uncertainty (grey area) as you go further back in time.
What The Science Says:
Since the hockey stick paper in 1998, there have been a number of proxy studies analysing a variety of different sources including corals, stalagmites, tree rings, boreholes and ice cores. They all confirm the original hockey stick conclusion: the 20th century is the warmest in the last 1000 years and that warming was most dramatic after 1920.
Climate Myth: Hockey stick is broken
“In 2003 Professor McKitrick teamed with a Canadian engineer, Steve McIntyre, in attempting to replicate the chart and finally debunked it as statistical nonsense. They revealed how the chart was derived from "collation errors, unjustified truncation or extrapolation of source data, obsolete data, incorrect principal component calculations, geographical mislocations and other serious defects" -- substantially affecting the temperature index.” (John McLaughlin)
The "hockey stick" describes a reconstruction of past temperature over the past 1000 to 2000 years using tree-rings, ice cores, coral and other records that act as proxies for temperature (Mann et al. 1999). The reconstruction found that global temperature gradually cooled over the last 1000 years with a sharp upturn in the 20th Century. The principal result from the hockey stick is that global temperatures over the last few decades are the warmest in the last 1000 years.

Figure 1: Northern Hemisphere temperature changes estimated from various proxy records shown in blue (Mann et al. 1999). Instrumental data shown in red. Note the large uncertainty (grey area) as you go further back in time.
A critique of the hockey stick was published in 2004 (McIntyre & McKitrick 2005), claiming the hockey stick shape was the inevitable result of the statistical method used (principal components analysis). They also claimed temperatures over the 15th Century were derived from one bristlecone pine proxy record. They concluded that the hockey stick shape was not statistically significant.
An independent assessment of Mann's hockey stick was conducted by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (Wahl & Ammann 2007). They reconstructed temperatures employing a variety of statistical techniques (with and without principal components analysis). Their results found slightly different temperatures in the early 15th Century. However, they confirmed the principal results of the original hockey stick - that the warming trend and temperatures over the last few decades are unprecedented over at least the last 600 years.
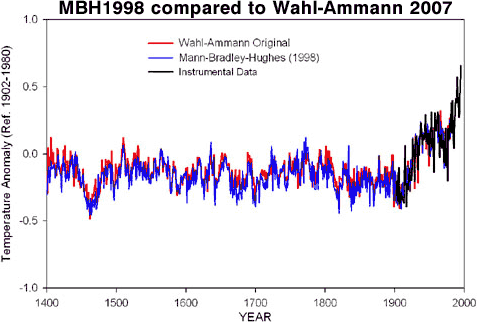
Figure 2: Original hockey stick graph (blue - MBH1998) compared to Wahl & Ammann reconstruction (red). Instrumental record in black (Wahl & Ammann 2007).
While many continue to fixate on Mann's early work on proxy records, the science of paleoclimatology has moved on. Since 1999, there have been many independent reconstructions of past temperatures, using a variety of proxy data and a number of different methodologies. All find the same result - that the last few decades are the hottest in the last 500 to 2000 years (depending on how far back the reconstruction goes). What are some of the proxies that are used to determine past temperature?
Changes in surface temperature send thermal waves underground, cooling or warming the subterranean rock. To track these changes, underground temperature measurements were examined from over 350 bore holes in North America, Europe, Southern Africa and Australia (Huang et al. 2000). Borehole reconstructions aren't able to give short term variation, yielding only century-scale trends. What they find is that the 20th century is the warmest of the past five centuries with the strongest warming trend in 500 years.
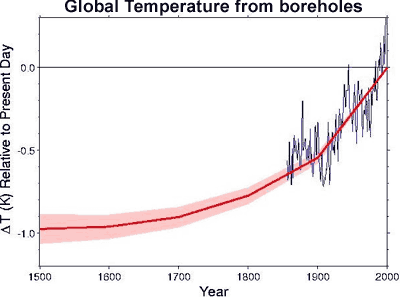
Figure 3: Global surface temperature change over the last five centuries from boreholes (thick red line). Shading represents uncertainty. Blue line is a five year running average of HadCRUT global surface air temperature (Huang et al. 2000).
Stalagmites (or speleothems) are formed from groundwater within underground caverns. As they're annually banded, the thickness of the layers can be used as climate proxies. A reconstruction of Northern Hemisphere temperature from stalagmites shows that while the uncertainty range (grey area) is significant, the temperature in the latter 20th Century exceeds the maximum estimate over the past 500 years (Smith et al. 2006).
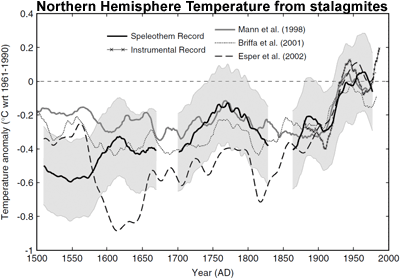
Figure 4: Northern Hemisphere annual temperature reconstruction from speleothem reconstructions shown with 2 standard error (shaded area) (Smith et al. 2006).
Historical records of glacier length can be used as a proxy for temperature. As the number of monitored glaciers diminishes in the past, the uncertainty grows accordingly. Nevertheless, temperatures in recent decades exceed the uncertainty range over the past 400 years (Oerlemans 2005).
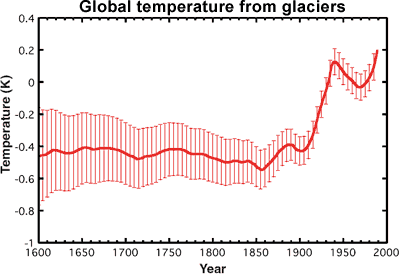
Figure 5: Global mean temperature calculated from glaciers. The red vertical lines indicate uncertainty.
Of course, these examples only go back around 500 years - this doesn't even cover the Medieval Warm Period. When you combine all the various proxies, including ice cores, coral, lake sediments, glaciers, boreholes & stalagmites, it's possible to reconstruct Northern Hemisphere temperatures without tree-ring proxies going back 1,300 years (Mann et al. 2008). The result is that temperatures in recent decades exceed the maximum proxy estimate (including uncertainty range) for the past 1,300 years. When you include tree-ring data, the same result holds for the past 1,700 years.
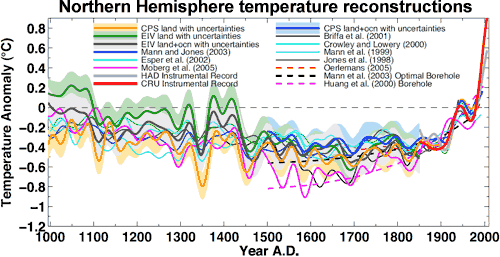
Figure 6: Composite Northern Hemisphere land and land plus ocean temperature reconstructions and estimated 95% confidence intervals. Shown for comparison are published Northern Hemisphere reconstructions (Mann et al. 2008).
Paleoclimatology draws upon a range of proxies and methodologies to calculate past temperatures. This allows independent confirmation of the basic hockey stick result: that the past few decades are the hottest in the past 1,300 years.
Intermediate rebuttal written by John Cook
 |
The Skeptical Science website by Skeptical Science is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. |