What The Science Says:
Despite the logarithmic relationship between CO2 and surface temperatures, atmospheric CO2 levels are rising so fast that unless we dramatically decrease our emissions, global warming will accelerate over the 21st Century.
Climate Myth: An exponential increase in CO2 will result in a linear increase in temperature
This logarithmic relationship means that each doubling of atmospheric CO2 will cause the same amount of warming at the Earth's surface. Thus if it takes as long to increase atmospheric CO2 from 560 to 1120 parts per million by volume (ppmv) as it did to rise from 280 to 560 ppmv, for example, then the associated warming at the Earth's surface will be roughly linear. So the question then becomes, how fast do we expect atmospheric CO2 to rise over the next century?
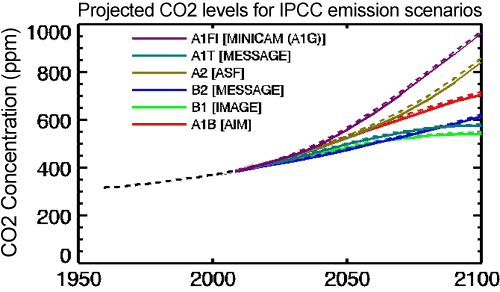
The IPCC addressed this question by examining a number of different anthropogenic emissions scenarios. Scenario A1F1 assumes high global economic growth and continued heavy reliance on fossil fuels for the remainder of the century. Scenario B1 assumes a major move away from fossil fuels toward alternative and renewable energy as the century progresses. Scenario A2 is a middling scenario, with less even economic growth and some adoption of alternative and renewable energy sources as the century unfolds. The projected atmospheric CO2 levels for these scenarios is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Atmospheric CO2 concentrations as observed at Mauna Loa from 1958 to 2008 (black dashed line) and projected under the 6 IPCC emission scenarios (solid coloured lines). (IPCC Data Distribution Centre)
In short, following the 'business as usual' approach without major steps to move away from fossil fuels and limit greenhouse gas emissions, we will likely reach 850 to 950 ppmv of atmospheric CO2 by the year 2100. It will have taken approximately 200 years (from 1850 to 2050) for the first doubling of atmospheric CO2 from 280 to 560 ppmv, but it will only take another 70 years or so to double the levels again to 1120 ppmv. This will result in an accelerating rate of global warming, not a linear rate. Under Scenarios A2 and A1F1, the IPCC report projects that the global temperature in 2095 will be 2.0–6.4°C above 1990 levels (2.6-7.0°C above pre-industrial), with a best estimate of 3.4 and 4.0°C warmer (4.0 and 4.6°C above pre-industrial average surface temperatures), respectively.
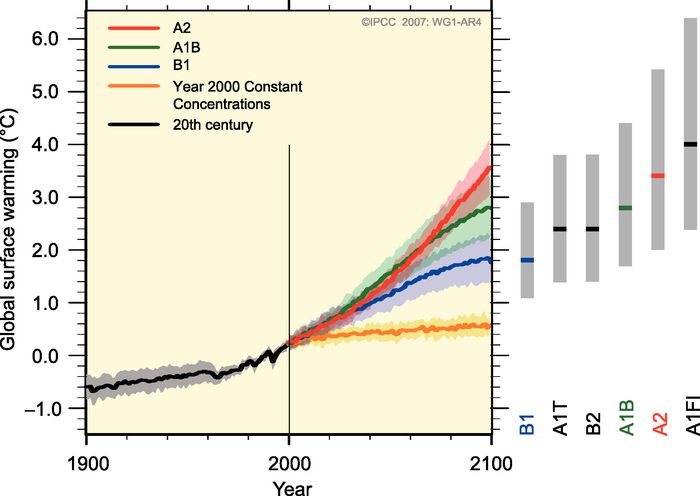
Figure 2: Global surface temperature projections for IPCC Scenarios. Shading denotes the ±1 standard deviation range of individual model annual averages. The orange line is constant CO2 concentrations at year 2000 values. The grey bars at right indicate the best estimate (solid line within each bar) and the likely range. (Source: IPCC).
Some skeptics have claimed that these projected amounts of warming have not been borne out in the surface temperature changes over the past decade. But there are many factors which impact short-term global temperatures, which may conceal the long-term warming caused by increasing atmospheric CO2. So if we want to know if the IPCC projections are realistic, rather than examining noisy short-term temperature data, we should examine how much atmospheric CO2 is increasing.
When we look at this data, we find that observed CO2 emissions in recent years have actually been tracking close to or above the worst case (A1F1) scenario.
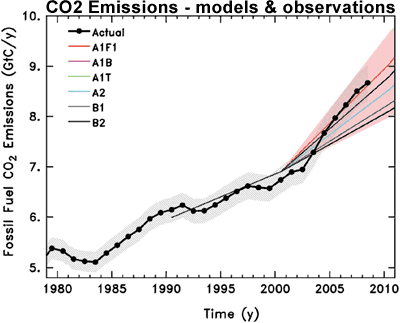
Figure 3: Observed global CO2 emissions from fossil fuel burning and cement production compared with IPCC emissions scenarios. The coloured area covers all scenarios used to project climate change by the IPCC (Copenhagen Diagnosis).
So if we continue in a business-as-usual scenario, we should expect to see atmospheric CO2 levels accelerate rapidly enough to more than offset the logarithmic relationship with temperature, and cause the surface temperature warming to accelerate as well. Cllaims of a linear increase in temperature ignore that in the 'business as usual' scenario, we are currently on pace to double the current atmospheric CO2 concentration (390 to 780 ppmv) within the next 60 to 80 years, and we have not yet even come close to doubling the pre-industrial concentration (280 ppmv) in the past 150 years. Thus the exponential increase in CO2 will outpace its logarithmic relationship with surface temperature, causing global warming to accelerate unless we take serious steps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In fact, to continue the current rate of warming over the 21st Century, we would need to achieve IPCC scenario B1 - a major move away from fossil fuels toward alternative and renewable energy.
 |
The Skeptical Science website by Skeptical Science is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. |