Tree-ring proxies and the divergence problem
What the science says...
| Select a level... |
 Basic
Basic
|
 Intermediate
Intermediate
| |||
|
The divergence problem is a physical phenomenon - tree growth has slowed or declined in the last few decades, mostly in high northern latitudes. The divergence problem is unprecedented, unique to the last few decades, indicating its cause may be anthropogenic. The cause is likely to be a combination of local and global factors such as warming-induced drought and global dimming. Tree-ring proxy reconstructions are reliable before 1960, tracking closely with the instrumental record and other independent proxies. |
|||||
Climate Myth...
Tree-rings diverge from temperature after 1960
Actual reconstructions "diverge" from the instrumental series in the last part of 20th century. For instance, in the original hockey stick (ending 1980) the last 30-40 years of data points slightly downwards. In order to smooth those time series one needs to "pad" the series beyond the end time, and no matter what method one uses, this leads to a smoothed graph pointing downwards in the end whereas the smoothed instrumental series is pointing upwards — a divergence (Climate Audit).
At a glance
"Trees tell of past climates: but are they speaking less clearly today?" That was the intriguing title of a paper published in the peer-reviewed journal, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, in 1998. The authors discussed various aspects of the use of tree-rings as representatives - or proxies - of past climatic patterns.
Tree growth is sensitive to temperature. Because of that, warmer wetter periods produce wider tree-ring patterns. When it's colder and dryer, the rings are narrower, indicating slow growth. In this way, the width and density of tree-rings in ancient trees serve as a proxy for temperature. That makes it possible to reconstruct temperature records going back over many centuries. For example, historic events such as major volcanic explosions tend to lead to global cooling. Such events show up very well in tree-ring reconstructions.
In more recent times, since the late 19th century, we also have the observational temperature record to compare with tree-ring reconstructions. Agreement between the two datasets is at first close. However, in middle and especially high latitude sites, the correlation breaks down after 1960. At this point, while temperatures rise, tree-ring width shows a falling trend - a decline. This divergence between temperature and tree growth is called, imaginatively enough, the divergence problem.
The decline, or divergence problem had been recognised, regularly discussed and written about since around 1995. That's 14 years before anyone had ever heard of 'climategate' and the song and dance that the science–deniers made of 'hide the decline'. If anything should serve as a quality-control alert for the output of science-deniers, it's right there.
Now, everything that happens has a cause, but not all causes are straightforward. There are plenty of ways to put stress on plants and stress makes growth-patterns abnormal. The trouble is that such stress-factors often vary in an irregular fashion and independently of one another. Even in a 2023 paper, the detailed cause of the divergence problem was described as being accompanied by 'significant controversies'. It's real, but it's complicated, in other words.
Temperature-induced drought stress and changes in seasonality are likely to be relevant here. Also likely to have had a role is the phenomenon of ‘Arctic dimming'. The term 'dimming' refers to reduced sunshine reaching the surface in some circumpolar regions, due to industrial aerosol pollution. Northern Hemisphere pollution tends to accumulate over the Arctic. Reduced sunshine affects photosynthesis and in return that impacts upon plant health and growth. Indeed, a 2021 paper ominously commented that the effects of Arctic aerosols on net primary production - growth - were particularly important in light of the current race to exploit natural resources north of the Arctic circle.
The extensive boreal forests of the north play a major role in shaping Earth’s carbon cycle and climate system. In the divergence problem, they have raised a red flag. Something up there is wrong and it should come as no surprise that, once again, our reckless misuse of our planet is high on the list of suspects for that.
Please use this form to provide feedback about this new "At a glance" section. Read a more technical version below or dig deeper via the tabs above!
Further details
"An anomalous reduction in forest growth indices and temperature sensitivity has been detected in tree-ring width and density records from many circumpolar northern latitude sites since around the middle 20th century". This phenomenon, also known as the “divergence problem”, is expressed as an offset between warmer instrumental temperatures and their underestimation in reconstruction models based on tree rings."
Can you guess when that was written?
It's the first few lines of the abstract of a review paper published in 2008. That's a year and nine months prior to all the manufactured controversy of so-called 'climategate', in which issues with tree-rings were seized upon by the usual suspects. But the issues are relatively recent. Here's an explainer.
Tree growth is sensitive to temperature. As a result, tree-ring width and tree-ring density, both indicators of tree growth, serve as useful proxies for temperature. By measuring tree growth in ancient trees, scientists can reconstruct temperature records going back over 1000 years. Comparisons with direct temperature measurements from 1880 to the present day show, for the earlier half of this period, a high correlation with tree growth. However, in high latitude sites, the correlation broke down after 1960. After this point, while observed temperatures rose decade on decade, tree-ring reconstructions showed a falling trend. This is what is known as the divergence problem.
The divergence problem has been discussed in the peer reviewed literature since the mid 1990s when it was noticed that Alaskan trees were showing a weakened temperature signal in recent decades (Jacoby & D'Arrigo 1995). This work was broadened in 1998 using a network of over 300 tree-ring records across high northern latitudes (Briffa et al. 1998). From 1880 to 1960, there is a high correlation between the instrumental record and tree growth. Over this period, tree-rings are an accurate proxy for climate. However, the correlation dropped off sharply after 1960. At high latitudes, there has been a major, wide-scale change in tree-growth over the past few decades.
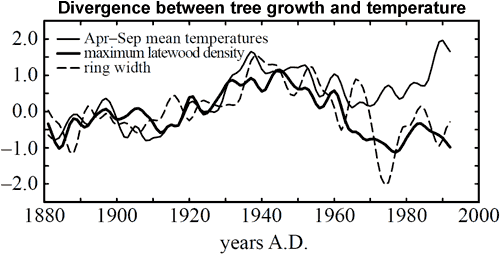
Figure 1: Twenty-year smoothed plots of tree-ring width (dashed line) and tree-ring density (thick solid line), averaged across a network of mid-northern latitude boreal forest sites and compared with equivalent-area averages of mean April to September temperature anomalies (thin solid line). Graphic from Briffa et al. 1998.
Has this phenomenon happened before? In other words, can we rely on tree-ring growth as a proxy for temperature? Briffa and colleagues show that tree-ring width and density show close agreement with temperature back to 1880. To examine earlier periods, one study split a network of tree sites into northern and southern groups (Cook et al. 2004). While the northern group showed significant divergence after the 1960s, the southern group was consistent with recent warming trends. This has been a general trend with the divergence problem - trees from high northern latitudes show divergence while low latitude trees show little to no divergence.
The important result from Cook et al was that before the 1960s, the groups tracked each other reasonably well back to the Medieval Warm Period. Thus, the study suggests that the current divergence problem is unique over the past thousand years and is restricted to recent decades.
That this is a relatively recent phenomenon suggests that the decline in tree growth may have at least a partial anthropogenic cause. A thorough review of the many peer reviewed studies investigating possible contributing factors can be found in 'On the ’divergence problem’ in northern forests: A review of the tree-ring evidence and possible causes' (D’Arrigo et al. 2008). Some of the findings of the review were as follows.
Various studies had noted the drop in Alaskan tree-growth coincided with an increase in warming-induced drought. Combined temperature and rainfall records showed that growth declines were more common in the warmer, drier locations. In addition, studies in Japan and Bavaria suggested that increased sulphur dioxide emissions had a role.
Indeed, as the divergence problem is widespread across high northern latitudes, there may be a large-scale explanation, possibly related to airborne pollution effects. A later study (Briffa et al. 2004) proposed that falling stratospheric ozone concentration was a possible cause of the divergence, since this observed ozone decline has been linked to an increased incidence of ultraviolet (UV-B) radiation at the ground.
Another factor at those high latitudes was what is known as global dimming - a drop in solar radiation reaching the ground. The average amount of sunlight reaching the ground declined by around 4 to 6% from 1961 to 1990. That is almost certainly down to aerosol-based industrial pollution.
One study suggested that microsite factors are an influence on whether individual trees are vulnerable to drought stress. Such factors included the slope where the tree is located, the depth to permafrost and other localised factors (Wilmking & Singh 2008). This paper amusingly refers to the divergence problem as the "divergence effect" so as "to not convey any judgement by the wording" (you wouldn't want to offend those overly sensitive Alaskan trees).
In summary, there is evidence for local, regional and global causes all being involved with the divergence problem. It's a complex combination of various contributing and interacting factors, often unique to different regions and even individual trees. At the time of writing, early 2024, it's still being discussed (e.g. Büntgen et al. 2021; Cai & Lu 2023; abstract in English). So that's what 'hide the decline' was all about. The divergence problem - a particularly complex issue with multiple interacting causes that affects tree-ring records since 1960. Fortunately, we have been able to directly measure and average out global temperature for over a century now, so we know it's warming anyway. But the divergence problem - the decline - is a fascinating area of research in its own right.
Last updated on 1 May 2024 by John Mason. View Archives































 Arguments
Arguments































Me again, my opponent sent me this message and was wondering if I could recieve a proper answer to it. I know tree rings dont ONLY respond to cold temperatures, but I dont have everything I need to make a compelling case.
What he said:
"if you look at the tree ring proxies, they are only effective during "cold periods. They chose to exclude MWP because the data model breaks down."
http://wattsupwiththat.com/2013/08/16/oh-mann-paper-demonstrates-that-tree-ring-proxy-temperature-data-is-seriously-compromised/
tkman0 @70, the following graph from the supplementary material of Mann 09 shows reconstructions using all data (red), excluding tree rings (blue), excluding seven particular proxies "skeptics" have objected to (brown), and excluding both all tree rings and the seven particular proxies (green):
You should note that excluding the tree rings, or excluding the 7 particular proxies makes virtually no difference to the reconstruction. Excluding both does, at various locations, but does not consistently do so in any particular direction. Sometimes it is warmer and sometimes colder. That may simply be a function of the low sample size. The fewer the proxies, the more erratic the signal both because regional temperatures vary more than global (or hemisperic) temperatures; and because the fewer the proxies, the greater the probability actual noise, ie, a non-temperature signal, will survive rather than being cancelled out by averaging. Despite this greater erraticness, however, even excluding both tree ring and the seven particular proxies does not result in any major change in recent reconstructions, nor lift the reconstructed temperature above that in the late twentieth century at any point. Its biggest change where there are enough proxies to consider the reconstruction informative (ie, where it has a solid line) appears to be an elimination of the cooling coincident with the Maunder Minimum, ie, a clear error.
This is not the only reconstruction without tree rings, and none of the reconstructions without tree rings show a significantly different story to that from other reconstructions. Ergo, whatever the merits of Cecile et al (the paper referred to above), it has little bearing on the overall picture of past temperatures.
tkman0 @70, the following graph from the supplementary material of Mann 09 shows reconstructions using all data (red), excluding tree rings (blue), excluding seven particular proxies "skeptics" have objected to (brown), and excluding both all tree rings and the seven particular proxies (green):
You should note that excluding the tree rings, or excluding the 7 particular proxies makes virtually no difference to the reconstruction. Excluding both does, at various locations, but does not consistently do so in any particular direction. Sometimes it is warmer and sometimes colder. That may simply be a function of the low sample size. The fewer the proxies, the more erratic the signal both because regional temperatures vary more than global (or hemisperic) temperatures; and because the fewer the proxies, the greater the probability actual noise, ie, a non-temperature signal, will survive rather than being cancelled out by averaging. Despite this greater erraticness, however, even excluding both tree ring and the seven particular proxies does not result in any major change in recent reconstructions, nor lift the reconstructed temperature above that in the late twentieth century at any point. Its biggest change where there are enough proxies to consider the reconstruction informative (ie, where it has a solid line) appears to be an elimination of the cooling coincident with the Maunder Minimum, ie, a clear error.
This is not the only reconstruction without tree rings, and none of the reconstructions without tree rings show a significantly different story to that from other reconstructions. Ergo, whatever the merits of Cecile et al (the paper referred to above), it has little bearing on the overall picture of past temperatures.
Thanks Tom, also the guy sent this back which I found more hilarious than frustrating:
Again this is a very sophisticated but deceptive argument.
What Mann has done is he has thousands of tree samples from the cold periods. He has 7 (or some other similar number) from the IGW period.
So yes, applying the samples from the IGW period doesn't change the results - because his his data is not valid or representative.
Do you get the point? I'll explain it more if you dont.
tkman0... I think it would be a good idea to get this person to cite his references so people can see where he's getting his information.
This last comment is as bizarre as I've seen, and I've seen a lot.
my thoughts exactly