 Arguments
Arguments
 Software
Software
 Resources
Comments
Resources
Comments
 The Consensus Project
The Consensus Project
 Translations
Translations
 About
Support
About
Support


Latest Posts
- Fact brief - Is climate change a net benefit for society?
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #16 2025
- Climate Adam: Climate Scientist Reacts to Elon Musk
- Sabin 33 #24 - Is wind power too expensive?
- EGU2025 - Picking and chosing sessions to attend on site in Vienna
- 2025 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #15
- Fact brief - Is the sun responsible for global warming?
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #15 2025
- Renewables allow us to pay less, not twice
- Sabin 33 #23 - How much land is used for wind turbines?
- Our MOOC Denial101x has run its course
- 2025 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #14
- Fact brief - Is Mars warming?
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #14 2025
- Two-part webinar about the scientific consensus on human-caused global warming
- Sabin 33 #22 - How does waste from wind turbines compare to waste from fossil fuel use?
- Clean energy generates major economic benefits, especially in red states
- 2025 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #13
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #13 2025
- Climate skeptics have new favorite graph; it shows the opposite of what they claim
- Sabin 33 #21 - How does production of wind turbine components compare with burning fossil fuels?
- China will need 10,000GW of wind and solar by 2060
- 2025 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #12
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #12 2025
- Climate Fresk - a neat way to make the complexity of climate change less puzzling
- Sabin 33 #20 - Is offshore wind development harmful to whales and other marine life?
- Do Americans really want urban sprawl?
- 2025 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #11
- Fact brief - Is waste heat from industrial activity the reason the planet is warming?
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #11 2025
Archived Rebuttal
This is the archived Advanced rebuttal to the climate myth "Temp record is unreliable". Click here to view the latest rebuttal.
What the science says...
|
Independent studies using different software, different methods, and different data sets yield very similar results. The increase in temperatures since 1975 is a consistent feature of all reconstructions. This increase cannot be explained as an ar |
There are three prominent reconstructions of monthly global mean surface temperature (GMST) from instrumental data (fig. 1): NASA's GISTEMP analysis, the CRUTEM analysis (from the University of East Anglia's Climatic Research Unit), and an analysis by NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC).
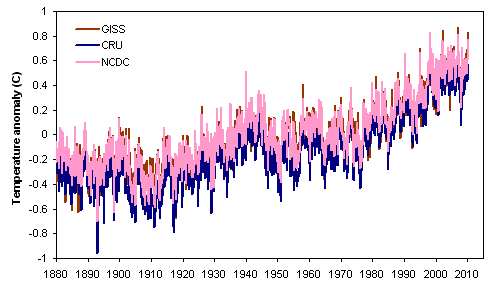
Figure 1. Comparison of global (land & ocean) mean surface temperature reconstructions from NASA GISS, the University of East Anglia's CRU, and NOAA NCDC.
How reliable are these temperature reconstructions? Various questions have been raised about both the data and the methods used to produce them. Now, thanks to the hard work of many people, we can conclude that the three global temperature analyses are reasonable, and the true surface temperature trend is unlikely to be substantially different from the picture drawn by NASA, CRU, and NOAA.
The three GMST analyses have much in common, though there are significant differences among them as well. All three have at their core the monthly temperature data from the Global Historical Climatology Network (GHCN), and all three produce both a land-stations-only reconstruction and a combined land/ocean reconstruction that includes sea surface temperature measurements.
Let's explore the reliability of these reconstructions, from several different angles.
The data and software used to produce these reconstructions are publicly available
Source code and data to recreate GISTEMP and CRUTEM are available from NASA and CRU websites. (The data set provided by CRU excludes a fraction of the data that were obtained from third parties, but the results are not substantially affected by this).
The software has been successfully tested outside of NASA and CRU, and it works as advertised
Both GISTEMP and CRUTEM have been successfully implemented by independent investigators. For example, Ron Broberg has run both the CRUTEM and GISTEMP code. In addition, the Clear Climate Code project has duplicated GISTEMP in Python. Figure 2 shows a comparison of the output of the GISTEMP reconstruction process as implemented by NASA and by Clear Climate Code ... but since the results are identical, the second line falls exactly on top of the first.

Figure 2. The GISTEMP land/ocean temperature analysis as implemented by NASA and by Clear Climate Code. Results of the two analyses are effectively identical.
Similar results can be obtained using different software and methods
Over the past year, there has been quite a flurry of "do-it-yourself" temperature reconstructions by independent analysts, using either land-only or combined land-ocean data. In addition to the previously-mentioned work by Ron Broberg and Clear Climate Code, these include the following:
(There are probably others as well that we're omitting!)
Most recently, the Muir Russell investigation in the UK was able to write their own software for global temperature analysis in a couple of days.
For all of these cases, the results are generally quite close to the "official" results from NASA GISS, CRU, and NOAA NCDC. Figure 3 shows a collection of seven land-only reconstructions, and Figure 4 shows five global (land-ocean) reconstructions.

Figure 3. Comparison of land-only reconstructions, 1900-2009. Note that the NASA GISS reconstruction using only land stations is not shown here, because it is conceptually different from the other analyses.

Figure 4. Comparison of land-ocean reconstructions, 1900-2009.
Obviously, the results of the reconstructions are quite similar, whether they're by the "Big Three" or by independent analysts.
The temperature increase is not an artifact of the GHCN adjustment process
Most of the analyses shown above actually use the raw (unadjusted) GHCN data. Zeke Hausfather has done comparisons using both the adjusted and raw versions of the GHCN data set, and as shown in fig. 5, the results are not substantially different at the global scale (though 2008 is a bit of an outlier).

Figure 5. Comparison of global temperatures from raw and adjusted GHCN data, 1900-2009 (analysis by Zeke Hausfather).
The temperature increase is not an artifact of declining numbers of stations
While it is true that the number of stations in GHCN has decreased since the early 1990s, that has no real effect on the results of spatially weighted global temperature reconstructions. How do we know this?
- Comparisons of trends for stations that dropped out versus stations that persisted post-1990 show no difference in the two populations prior to the dropouts (see, e.g., here and here and here).
- The spatial weighting processes (e.g., gridding) used in these analyses makes them robust to the loss of stations. In fact, Nick Stokes has shown that it's possible to derive a global temperature reconstruction using just 61 stations worldwide (in this case, all the stations from GISTEMP that are classified as rural, have at least 90 years of data, and have data in 2010).
- Other data sets that don't suffer from GHCN's decline in station numbers show the same temperature increase (see below).
One prominent claim (by Joe D'Aleo and Anthony Watts) was that the loss of "cool" stations (at high altitudes, high latitudes, and rural areas) created a warming bias in the temperature trends. But Ron Broberg conclusively disproved this, by comparing trends after removing the categories of stations in question. D'Aleo and Watts are simply wrong.
The temperature increase is not an artifact of stations being located at airports
This might seem like an odd statement, but some people have suggested that the tendency for weather stations to be located at airports has artificially inflated the temperature trend. Fortunately, there is not much difference in the temperature trend between airport and non-airport stations.
The temperature increase is present in other data sets, not just GHCN
All of the above studies rely (mostly or entirely) on monthly station data from the GHCN database. But it turns out that other, independent data sets give very similar results.

Figure 6. Comparison of global temperatures from the Global Historical Climatology Network (GHCN) and Global Summary of the Day (GSOD) databases. (Analysis by Ron Broberg and Nick Stokes).
What about satellite measurements of temperatures in the lower troposphere? There are two widely cited analyses of temperature trends from the MSU sensor on NOAA's polar orbiting earth observation satellites, one from Remote Sensing Systems (RSS) and one from the University of Alabama-Huntsville (UAH). These data only go back to 1979, but they do provide a good comparison to the surface temperature data over the past three decades. Figure 7 shows a comparison of land, ocean, and global temperature data from the surface reconstructions (averaging the multiple analyses shown in figs. 3 and 4) and from satellites (averaging the results from RSS and UAH):

Figure 7. Comparison of temperatures from surface stations and satellite monitoring of the lower troposphere.
A paper by by Anderson et al. (2012) created a new global surface temperature record reconstruction using 170 records with some type of physical or biological link to global surface temperatures (corals, ice cores, speleothems, lake and ocean sediments, and historical documents). The study compared their reconstruction to the instrumental temperature record and found a strong correlation between the two (0.76).
Figure 8. Paleo Index (solid) and the merged land-ocean surface temperature anomalies (MLOST, dashed) relative to 1901-2000. The range of the paleo trends index values is coincidentally nearly the same as the GST although the quantities are different (index values versus temperature anomalies °C).
We'll end by looking at all the surface and satellite-based temperature trends over the entire period for which both are available (1979-present). What are the trends in the various data sets and regions? As shown in fig. 9, the surface temperature trends over land have a fair amount of variability, but all lie between +0.2 and +0.3 C/decade. Surface trends that include the oceans are more uniform.

Figure 9. Comparison of temperature trends, in degrees C per decade.
Overall, the satellite measurements show lower trends than surface measurements. This is a bit of a puzzle, because climate models suggest that overall the lower troposphere should be warming about 1.2X faster than the surface (though over land there should be little difference, or the surface should be warming faster). Thus, there are at least three possibilities:
- The surface temperature trends show slightly too much warming.
- The satellite temperature trends show slightly too little warming.
- The prediction of climate models (about amplified warming in the lower troposphere) is incorrect, or there are complicating factors that are being missed.
It should be noted that in the past the discrepancy between surface and satellite temperature trends was much larger. Correcting various errors in the processing of the satellite data has brought them into much closer agreement with the surface data.
Conclusions
The well-known and widely-cited reconstructions of global temperature, produced by NASA GISS, UEA CRU, and NOAA NCDC, are replicable.
Independent studies using different software, different methods, and different data sets yield very similar results.
The increase in temperatures since 1975 is a consistent feature of all reconstructions, and is also a feature found in reconstructions from natural temperature proxy measurements. This increase cannot be explained as an artifact of the adjustment process, the decrease in station numbers, or other non-climatological factors.
Sources
- GISTEMP
- CRUTEM
- NCDC global temperature series
- RSS
- UAH
- Results from individual reconstructions, compiled by Zeke Hausfather
Updated on 2013-01-02 by dana1981.
THE ESCALATOR

(free to republish)

























































