Does CO2 always correlate with temperature (and if not, why not?)
What the science says...
| Select a level... |
 Basic
Basic
|
 Intermediate
Intermediate
| |||
|
Surface temperature measurements are affected by short-term climate variability, and recent warming of deep oceans |
|||||
Climate Myth...
There's no correlation between CO2 and temperature
"Twentieth century global warming did not start until 1910. By that time CO2 emissions had already risen from the expanded use of coal that had powered the industrial revolution, and emissions only increased slowly from 3.5gigatonnes in 1910 to under 4gigatonnes by the end of the Second World War.
It was the post war industrialization that caused the rapid rise in global CO2 emissions, but by 1945 when this began, the Earth was already in a cooling phase that started around 1942 and continued until 1975. With 32 years of rapidly increasing global temperatures and only a minor increase in global CO2 emissions, followed by 33 years of slowly cooling global temperatures with rapid increases in global CO2 emissions, it was deceitful for the IPCC to make any claim that CO2 emissions were primarily responsible for observed 20th century global warming." (Norm Kalmanovitch).
At a glance
If you happen to be reading something about climate change in the popular media, be sure to keep an eye out for certain words. The one in this case is 'deceitful'. Why? Because it's an emotive word. It's a good sign that the writer is not a scientist but someone with a political axe to grind.
The heat-trapping properties of carbon dioxide, water vapour and other greenhouse gases were identified over 160 years ago. After that, climate research continued unhindered for many decades. However, by the second half of the 20th century the seriousness of the threat of climate change was well-understood. That led in due course to the involvement of bodies such as the United Nations. Treaties such as the Kyoto Protocol of 1997 followed.
In response, the fossil fuels sector and their political and media associates, perceiving threats to profitability, turned climate science into a political football. With climate science thus politicised, the arena within which research and outreach were conducted had changed. This was no longer a quiet backwater.
That's the historical context. Now we can get to the meat of the myth. The quote above this piece dates from September 2009. Apart from anything else, it's 14 years out of date now. Globally, the ten warmest years since 1880 have all occurred since the statement was made. According to NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies, the average global temperature has increased by 1.4° Celsius (2.5° Fahrenheit) since 1880.
However, global temperature does not correlate exactly with CO2 emissions on a year in, year out basis.There are other well-understood factors that can warm or cool the climate over such short-term periods. You may have heard of El Nino and La Nina. These phenomena involve above- or below-average sea surface temperatures respectively, in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. Their effects are global.
A strong El Nino can produce a massive global temperature-spike. Such very warm years once led to people making the claim of, "no warming since 1998". Briefly sounding plausible for a few years, it soon became self-evidently incorrect.
Instead, the correct way to look at temperature trends is to examine them over multiple decades - 30 years is standard in climate science. So to answer the question, "where are we now?", one would look at the temperature record from 1992-2022. Doing so takes out the noise, the ups and downs due to El Nino, La Nina and other factors. And the trend is most certainly upwards.
To the newcomer to climate science, it can be difficult to spot misinformation. However, opinion-pieces that accuse bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) of intentions like deceit should instantly ring alarm-bells.
It is important to point out that the motive for such political misinformation is to spread confusion and doubt. The organisations behind it simply seek delaying any meaningful action. In kicking the can down the road, they try to deflect the pressure to get their own houses in order, and to hell with the consequences.
Please use this form to provide feedback about this new "At a glance" section. Read a more technical version below or dig deeper via the tabs above!
Further details
The amount of CO2 in our atmosphere is increasing all the time. On February 26th 2024, according to the monitoring resource Daily CO2, it had exceeded 425 parts per million (ppm). That's up by 3.96 ppm since the same time last year - but more importantly, up from around 280 ppm before the industrial revolution - a 50% plus increase.
Pre-industrial levels of CO2 and other greenhouse gases, like methane and water vapour, were sufficient to keep the Earth’s surface 30°Celsius (54°F) warmer than it would have been without them. Since then, we have added 50% more CO2 - but that doesn't mean the temperature will go up by 50% too.
There are several reasons why. Doubling the amount of CO2 does not double the greenhouse effect. The way the climate reacts is also complex and it can be difficult to separate the effects of natural changes from man-made ones over short periods of time.
As the amount of man-made CO2 goes up, temperatures rise but not at the same rate. Estimates vary - climate sensitivity is a hot topic in climate science, if you’ll forgive the pun. Based on multiple lines of evidence, according to the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (2021), the "very likely range [for climate sensitivity to doubling of CO2] is 2°C to 5°C".
So far, the average global temperature has gone up by about 1.4 degrees C (2.5 F).
"In 2023, hundreds of millions of people around the world experienced extreme heat, and each month from June through December set a global record for the respective month. July was the hottest month ever recorded. Overall, Earth was about 2.5 degrees Fahrenheit (or about 1.4 degrees Celsius) warmer in 2023 than the late 19th-century average, when modern record-keeping began."
Source: NASA.
The speed of the increase is worth noting too. Unfortunately, as this quote from NASA demonstrates, anthropogenic climate change is happening very quickly compared to changes that occurred in the past (text in bold for emphasis):
"As the Earth moved out of ice ages over the past million years, the global temperature rose a total of 4 to 7 degrees Celsius over about 5,000 years. In the past century alone, the temperature has climbed 0.7 degrees Celsius, roughly ten times faster than the average rate of ice-age-recovery warming."
Source: NASA Earth Observatory.
Small increases in temperature can be hard to measure over short periods, because they can be masked by natural variation. For example, cycles of warming and cooling in the oceans such as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cause temperature changes that can mask small changes in temperature caused by CO2 emissions that occur at the same time. That's why scientists measure changes over long periods so that the effects of short natural variations can be distinguished from the effects of man-made CO2.
The rate of surface warming varies year by year, yet the physical properties of CO2 and other greenhouse gases do not change. Neither has the amount of energy arriving from the sun changed significantly in recent decades. But if that’s true, where is this heat going?
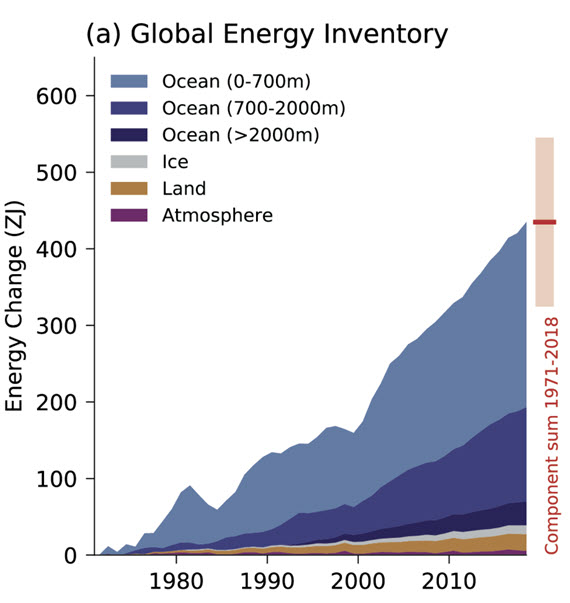
The answer is into the oceans. Fig. 1 is a graphic showing where the heat is currently going:
Figure 1: Global Energy Inventory: observed changes in the global energy inventory for 1971–2018 (shaded time series) with component contributions as indicated in the figure legend. Cross-Chapter Box 9.1 Figure 1 (part a) - From IPCC AR6 WGI Chapter 9.
The way heat moves in the deep oceans was poorly understood up until around the turn of the millennium. Since then, vast improvements in measurement techniques, such as the Argo float system, have allowed scientists to far more accurately gauge the amount of energy the oceans are absorbing. Argo floats, numbering several thousands, weigh 20-30 kilograms and are packed with instruments. They typically travel through the oceans around a kilometre below the surface. But they can rise up to the surface or dive down to 2 km. That makes it possible to collect profiles in terms of temperature, salinity and other parameters. So far, over two million such data-profiles have been collected.
Argo data have shown the upper 2,000 metres of the oceans has captured roughly 90% of the anthropogenic change in ocean heat content since the programme started in 1999. Temperatures in the upper 600 metres have been seen to fluctuate with shorter-term climate events like El Niño-Southern Oscillation. In deeper waters, however, there is a more consistent warming trend. In summary, the 700–2,000 metres ocean layer accounts for approximately one-third of the warming of the whole 0–2000 m layer of the World Ocean being mapped by the Argo floats.
So we know that the energy added to the climate system by man-made CO2 is not only apportioned into surface warming, because a large part of the heat goes into the oceans. The rate at which surface temperatures go up is not proportional to the rate of CO2 emissions but to the cumulative total amount of atmospheric CO2. Only by looking at long-term trends - 30 years is the standard period in climate science - can we measure surface temperature increases accurately, and distinguish them from short-term natural variation.
Last updated on 10 March 2024 by John Mason. View Archives































 Arguments
Arguments




































Regarding the energy budget shown by Tom Curtis at 140 I have a question. The IR radiation from the earth is 398.2, and the back radiation is 340.3, for a delta of 57.9 into the atmosphere. But the total outgoing IR radiation from the atmosphere is 239.9. So where does the additonal 182 (239.9-57.9) come from?
151 rkrolph:
You have to include all the energy fluxes into and out of the atmosphere!
The energy input includes absorbed incoming solar radiation (77.1), absorbed radiation from the surface (358.2), thermals (18.4) and latent heat in water vapour (86.4), totalling 540.1.
The energy loss includes back radiation to the surface (340.3) and radiation to space (169.9 + 29.9), again totalling 540.1.
The atmospheric window (40.1) represents radiation that passes directly from the surface to space without being absorbed by GHGs or clouds, and should not be counted here.
152 HK:
Thanks for clarifying that. I missed the 77.1 solar absorption number. I think then I would have figured out how the numbers work. That's my excuse anyway! :)
rkrolph @151, you probably have picked this up, but it is important to the budget that it contains three layers, the TOA, atmosphere, and Surface. In order, the budgets are (with all values in units of W/m^2):
TOA: 340.4 Solar in - (77.0 Solar reflected from clouds and atmosphere + 22.9 Solar reflected from the surface + 239.9 IR out) = 0.6
Atmosphere: (77.1 Solar absorbed by atmosphere + 358.2 Surface IR absorbed by atmosphere + 18.4 thermals + 86.4 latent heat) - ( 169.9 upward IR from atmosphere + 29.9 IR upward IR from clouds + 340.3 back radiation) = 0
Surface: (163.3 solar absorbed at surface + 340.3 back radiation from atmosphere) - (398.2 IR emitted from surface + 18.4 thermals + 86.4 latent heat) = 0.6
In addition, it is very important that the energy imbalance (right hand term in the equations) in the atmosphere plus the energy imbalance at the surface equals the energy imbalance at the TOA. If it did not, we would have a violation of conservation of energy. As a side note, it is also important that solar energy in equal solar energy reflected plus solar energy absorbed.
Some AGW deniers look at this diagram and say some element should be completely excluded as non-existent - most typically the back radiation. In doing so they merely show they do not consider conservation of energy to apply in climatology. You cannot remove a major element without creating an unaccounted for imbalance.
john warner has made such a suggestion (in his deleted coment @146) that:
Again, that fails the conservation of energy test. The total energy that needs to be replaced in the atmosphere is the combination of IR radiation to space from atmosphere and clouds (199.8) and the total value of the back radiation (340.3), but as the budget shows, that is indeed what is replaced.
Finally, it should be noted that many values in the graph are determined by a combination of observations plus the knowledge that they balance. Thus, due to calibration errors of absolute values, space born instruments show an imbalance of 1 - 2 W/m^2 between incoming and outgoing energy. The far more accurate observations of changes in ocean heat content are known to effectively identical with the actual TOA imbalance (within error), and are used with the knowledge that total surface plus atmosphere absorbed must equal the TOA imbalance to calibrate the actual TOA imbalance. Thus the precise concordance of the values is not evidence of anything but the researchers knowledge that the budget must not violate conservation of energy. The values are, however, sufficiently well constrained from observation that the removal of an entire form or energy transfer would violate not only conservation of energy but known observations.
Tom Curtis @150 No I never said anything like that. [snip] Why RH snipped the comment is beyond my ability to comprehend.
What I said in John Warner @ 146 is: Since the earth atmosphere radiates 199.8wpsm to space, 199.8wpsm has to be added to maintain the attained air temperature. 199.8wpsm is sufficient to maintain the entire vertical temperature structure of the atmosphere.
I don’t think either of Tom’s options were adequate and I had two comments prepared to defend my statement [snip] before the moderator suspended my privilege to speak. An email I sent to the Washington Free Beacon, based upon the NASA 1998 Solar Energy Budget, to remind everyone that the air temperature is based upon the joules of energy in the air. Furthermore, the 199.8wpsm represents the radiation to space of the entire atmosphere. In order to use the 1976 Standard Atmosphere Calculator Digital Dutch I had to enter 5,891 meters altitude. The temperature calculated by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law Calculator is a representative average annual global temperature for the entire atmosphere. The vertical temperature structure of the Troposphere up to 11 Kilometers is explained by the Ideal Gas Law. Tom incorrectly added that the temperature differential was the standard theoretical greenhouse effect. My second comment addresses Tom’s linear regression of the carbon dioxide sensitivity coefficient, using the Earth Air Budget, the Solar Energy Budget, the Standard Atmosphere Calculator and the Stefan-Boltzmann Law Calculator.
In short my belief is consistent with my reading of option 1 but is not limited by an unreasonable reading of option 1.
[RH] Moderation complaints snipped.
Tom Curtis @ 150 No I never said anything like that. [snip] It is beyond my capability to imagine what the moderator thought I meant. It would be nice if he would repost it.
What I said in John Warner @ 146 is: Since the earth atmosphere radiates 199.8wpsm to space, 199.8wpsm has to be added to maintain the attained air temperature. 199.8wpsm is sufficient to maintain the entire vertical temperature structure of the atmosphere.
I don’t think either of Tom’s options were adequate and I had two comments prepared to defend my statement [snip] before the moderator suspended my privilege to speak. An email I sent to the Washington Free Beacon, based upon the NASA 1998 Solar Energy Budget, to remind everyone that the air temperature is based upon the joules of energy already in the air. Furthermore, the 199.8wpsm represents the radiation to space of the entire atmosphere. In order to use the 1976 Standard Atmosphere Calculator Digital Dutch I had to enter 5,891 meters altitude. The temperature calculated by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law Calculator is a representative average annual global temperature for the entire atmosphere. The vertical temperature structure of the Troposphere up to 11 Kilometers is explained by the Ideal Gas Law. Tom incorrectly added that the temperature differential was the standard theoretical greenhouse effect. My second comment addresses Tom’s linear regression of the carbon dioxide sensitivity coefficient, using the Earth Air Budget, the Solar Energy Budget, the Standard Atmosphere Calculator and the Stefan-Boltzmann Law Calculator.
In short my belief is consistent with my reading of option 1 but is not limited by an unreasonable reading of option 1.
[PS] You are permitted to continue to defend your position here so long as you don't suddenly switch to another tack as you did over the question of ocean outgassing, and so long as follow the comments policy.
[RH] Moderation complaints snipped. Once again, John, we want you to focus in on one single issue here before gishgalloping in 16 other directions. It has been explained to you that your ideas are in contradiction with thermodynamic law relative to atmospheric air pressure. Set everything else to the side and deal with this one thing and then you can move onto others. If you cannot address this issue then you're going to have to relinquish your posting privileges. Nothing you've stated here or in the previously snipped comment have sufficiently addressed this and therefore, as warned, was deleted.
Tom Curtis @ 150 No
john warner @ 155/156.
Your first paragraph is undoubtedly incorrect.
Firstly, the atmosphere is insensitive to up or down. So in addition to radiating 200W/sq m upwards, it also radiates 200W/sq m downwards. It thus requires 400W/sq m to maintain a temperature of theoretically -40ºC (as Stefan-Boltzmann)
Secondly, it is incorrect to assert that even this 400W/sq m is sufficient to maintain "the entire vertical temperature structure of the atmosphere" unless you have some extra information to share with us. Your second paragraph does not suffice. Note this temperature you consider to be the average for an atmosphere with higher density (& thus thermodynamically averaged) at lower altitudes: such a theoretical atmosphere you imply has a temperature much closer to the tropopause than the surface.
Consider the simplest 'structure' possible, a two-layer atmosphere comprising a 'top' atmosphere and a 'bottom' atmosphere both opaque to the IR they absorb/radiate. The 'top' radiates 200W/sq m into space and thus has an average temperature of -40ºC, the 'bottom' radiates 340W/sq m back to the surface and thus has an average temperature of +5ºC. The imbalance at the interface between 'top' & 'bottom' atmoshpere would be (200 x 2) - 340 = 60W/sq m. The imbalance between the 'bottom' atmosphere and the surface woud be (340 x 2) - 200 - 360 = 120W/sq m. These two imbalances require further atmospheric heating which is provided by the absorbed solar radiation (75W/sq m) and the convection-driven energy flux (105W/sq m sensible & latent heat). As the tropopause marks the point where the convective process ends, the 60W/sq m required by the 'top' atmosphere cannot be solely solar in origin. Indeed the solar heating is predominantly below 6km and thus would not be predominantly heating the 'top' (see for instance Lacis & Hansen 1973 'A Parameterisation of the Absorption of Solar Radiation in the Earth's Atmosphere')
Of course, what this simplest of model is beginning to describe is the "standard theoretical greenhouse." but which is described within the second paragraph @155/156 as being incorrect. Perhaps my description here will allow the reason for this claim that "Tom (@149) incorrectly added that the temperature differential was the standard theoretical greenhouse effect." to be justified, which is certainly required as it is looking mighty wrong without it.
john warner @155 (156 &157 being redundant):
1)
What is necessary to maintain the vertical temperature structure is that the net energy balance of the atmosphere, ie, energy inputs minus energy outgoings, should equal zero. Given that, let's look at the energy balance again:
The energy input into the atmosphere is 77.1 Solar absorbed by atmosphere + 358.2 Surface IR absorbed by atmosphere + 18.4 thermals + 86.4 latent heat, for a total of 540.1 W/m^2. Given that, it is very clear that the 199.8 W/m^2 of upward IR emission from the atmosphere is insufficient to maintain a constant energy content in the atmosphere, and consequently a stable temperature structure. Without the 340.3 W/m^2 IR radiation from the atmosphere to the surface, that energy balance cannot be maintained, and consequently neither can the stable temperature structure.
This is so basic, and so simple, a point that if you are not able to acknowledge it, no further discussion with you is warranted nor capable of being fruitful.
2)
That the temperature differential, ie, the convection induced lapse rate in tropospheric temperatures is a corner stone of the standard theory of the greenhouse effect is seen in the seminal paper by Manabe and Weatherald (1967). David Archer and Raymond Pierrehumbert introduce that paper in their collection of seminal papers on global warming by saying (in part):
It is fair to say from that, that in their opinion without "a means ... to represent the effects of convection on the temperature structure of the atmosphere", a sound estimate (ie, one with an adequate theoretical grounding) is not possible. Therefore that temperature structure is fundamental to the basic theory of the greenhouse effect.
Indeed, absent that knowledge, it is impossible to predict event the sign of the effect of increased greenhouse gas concentrations on surface temperatures. If the lapse rate were negative (ie, temperatures increased with altitude), increased GHG concentration cools the surface, as in fact happens on Titan.
MA Rodger @158:
Any body of gas which has the same temperature throughout will radiate the same amount up and down, as emission is indifferent to direction. The atmosphere, however, has a distinct vertical temperature and density structure which results in a substantially greater downward emission at the bottom of the atmosphere than the upward emission at the top.
I am very certain you know this, but as written, your comment is likely to cause confusion, IMO.
Tom Curtis @160.
Suffice to say that we two surely are in agreement concerning the physics of the atmosphere but purely differ in how best to describe that physics for those who are easily confused by that physics. (I would ordinarily here set out my understanding of that difference-in-description but that may not be helpful in the circumstance.)
"...radiate the same amount up and down, as emission is indifferent to direction"
It is even so indifferent that it emits at the same intensity in all directions: up, down, left, right, etc.
Think of each point in space like a light bulb: casting radiation in all directions, shining outward onto an increasingly large sphere. The emission is then per unit solid angle (think of a cone facing out, with the tip at the source).
When you then want to know how much is arriving at a point, you need to think of it coming in from a sphere to the centre point, from all directions (not just up/down). The half-sphere (aka a hemisphere) that faces up is the downwelling radiation; a hemisphere facing down is the up-welling radiation.
The up/down division is the simplest way of focussing on the climatologically-important sums. Straight down, down at an angle, etc is all still down, and the same goes for up. Once you get one of your best mathematics friends to do the two-dimensional (in spherical coordinates) integration, you can divide the process up into what radiation climatologists call "the two-stream approximation" to get your up/down terms.
(Make sure its a good friend: the math is ugly for the amateur. Did I mention it's two-dimensional? And in spherical coordinates? That means trigonometry...)
In 2010 NASA published the Earth Energy Budget based upon the Clouds and the Earth Radiation Energy System mission. The surface air emits 358.2wpsm at a temperature of 281.93 degrees Kelvin. This is 158.4wpsm more than the solar power heating the earth air, 199.8wpsm. And 38.29 degrees Kelvin hotter than the 243.64 degrees Kelvin of the earth’s total air. The ideal gas law fully explains why increasing the pressure of a gas can increase the density and temperature. The 1976 Standard Atmosphere Calculator Digital Dutch confirms the correspondence between the theory and reality. Unlike the total air radiating to space and requiring an equal influx of solar energy to maintain the temperature, the surface air is radiating to the surface below and the air above. When the surface air is in equilibrium with its surroundings the temperature does not change because they are radiating equally against each other. There is no net flow of energy into and out of the surface air. So where does the energy come from to radiate in the first place. Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy in matter. The coefficient of heat content in air is one joule of energy for each degree Kelvin for one gram of air. Therefore each gram of air has the 281.93 joules of energy necessary to radiate at 358.2wpsm. In short, I don’t have to prove anything. The temperature of the air is sufficient proof that it has the energy to radiate at the rate specified by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law. Therefore 199.8wpsm is sufficient to maintain the attained total air temperature and to maintain the vertical temperature structure of the air. And even more important the ideal gas law description of the adiabatic lapse rate proves that greenhouse gases absorbed energy does not transfer through the atmosphere any differently than thermals or latent heat.
[RH] This scattered comment does not sufficiently address your current task at hand, which is to clearly address how your ideas contradict basic thermodynamics. I'm setting this as a warning so folks can continue to read what you've written. Patience for your ramblings has grown very thin here. Either clean up your act by more clearly and effectively explaining your position or you will have to relinquish your commenting privileges.
MA Rodger is very patiently pointing out errors. Carefully look through those and try to understand your errors.
john warner @163.
I highlight the task set you by the moderators. They said “It has been explained to you that your ideas are in contradiction with thermodynamic law relative to atmospheric air pressure. Set everything else to the side and deal with this one thing and then you can move onto others.”
Working backwards through your comment.
♣ - 1 - The lapse rate does demonstrate that upwards sensible heat transfer is a net flux resultant from the vertical temperature/pressure profile as is the radiative heat transfer. However, the latent heat transfer is not. Also I am at a loss as to why any of this is considered important.
♣ - 2 - Temperature does set radiant heat transfers.
♣ - 3 - You do not have to prove anything but without proof we will consider your statements as worthless.
♣ - 4 - The energy content of a gram of air may be (will always be) sufficient to radiate at a certain wattage for a certain period of time but this is not relevant to any physical process occuring in the atmosphere.
♣ - 5 - Yes, atmospheric temperatures can be considered in equilibrium but you leave unanswered what is maintaining the atmospheric energy.
♣ - 6 - There is a web-calculator of atmospheric temperature-pressure. What its calculations demonstrate/confirm is not described but is presumably not controversial.
♣ - 7 - Ideal gas laws do concern P, T & D.
♣ - 8 - The Earth Energy Budget does require satellite measurements but it employs a far broader set of data.
♣ - 9 - The graphic up-thread @159 (which does not date to 2010 but rather 2013/4) shows the atmosphere absorbing “358.2wpsm” which has no relation to any temperature calculated using S-B as it is absorbed radiation not emitted radiation. The “358.2wpsm” is greater than the sum of atmospheric heating (direct solar and net atmospheric heating) but the “358.2wpsm” is balanced by a “340.3wpsm” flux in the opposite direction.
john warner, given the task set by the moderators, I see no progress @163. Perhaps the individual points I make here will allow some direction to any forthcoming explanation.
164. MA Rodger
"♣ - 3 - You do not have to prove anything but without proof we will consider your statements as worthless."
I guess that applies to all of us. So, can you provide the proof for the claim that co2 can increase the temperature of the heat source heating it?
Not proof of absorption, proof of temperature increasing from only co2. Experimental data. There is lots of data from experimental studys of co2, I have still not found anything in there supporting that claim.
Absorption is well documented.
Increasing temperature, nope.
Would you please provide the scientific proof of the foundation of your claims? Where are the experiments showing how co2 increase temperature?
If you don´t have any, I guess your statements is a bit weak as well. Since the only thing you have is a weak and very short correlation of doubtful quality. That is the only argument you have, a correlation. That is hardly science.
If I put a bowl of Ice in a warm room, it will absorb and emit energy. Do you mean that it also increase temperature?
Tom Curtis at 23:49 PM on 15 December, 2016
"The energy input into the atmosphere is 77.1 Solar absorbed by atmosphere + 358.2 Surface IR absorbed by atmosphere + 18.4 thermals + 86.4 latent heat, for a total of 540.1 W/m^2. Given that, it is very clear that the 199.8 W/m^2 of upward IR emission from the atmosphere is insufficient to maintain a constant energy content in the atmosphere, and consequently a stable temperature structure. Without the 340.3 W/m^2 IR radiation from the atmosphere to the surface, that energy balance cannot be maintained, and consequently neither can the stable temperature structure."
Seriously, have you heard of heat transfer?
Don´t you know that the difference is found in the rate of transfer?
If you have 200W at tropopause and 400W at the surface, the difference of 200W is accounted for in the heat transfer. The surface uses 400W for it´s own temperature and on top of that it transfers 200W/m^2 to the atmosphere. That is basic heat transfer physics.
Where in the litterature do you find support for the claim that a decreasing flux from the atmosphere (a few watts) caused by co2, can affect the surface temperature? All I can find is that it is the other way around.
You know that increasing absorption, what you call an increase in radiative imbalance, always means that the absorber has gotten relatively colder? Also basic heat transfer physics.
Decreasing absorption and increasing flux from the atmosphere, that would be a sign of warming. You are making an argument about how co2 cools earth.
HK at 06:01 AM on 14 December, 2016
"You have to include all the energy fluxes into and out of the atmosphere!
The energy input includes absorbed incoming solar radiation (77.1), absorbed radiation from the surface (358.2), thermals (18.4) and latent heat in water vapour (86.4), totalling 540.1.
The energy loss includes back radiation to the surface (340.3) and radiation to space (169.9 + 29.9), again totalling 540.1."
And yet you use a fudge factor called albedo. Trenberth himself makes no secret of how they adjust albedo to cover up for imbalance.
How can anyone make an argument of "540.1" when ~~~~30% is yanked from the input value without justification from real measurements?
540W/m^2, that is a really low value for incident radiation. I want to see how the greenhousemodel calculate instantaneous radiation. In reality we have a real sun heating the surface at closer to 1000W/m^2 than 500.
HB @167 claims:
In fact, the outgoing Short Wave radiation at the Top Of the Atmosphere is measured by the CERES instrument flown on the Terra and Aqua satellites. Together with Total Solar Irradiation (TSI) data from the TIM instrument, that allows the direct calculation of the energy balance and albedo as:
Energy balance = TSI/4 - (OLWR + OSWR)
Albedo = (TSI - 4 x OSWR)/TSI,
where OLWR is Outgoinging Long Wave Radiation, and OSWR is Outgoing Short Wave Radiation.
TSI is divided 4 in the energy balance equation as it is measured relative to a flat plane perendicular to the incoming radiation, and needs to be averaged over the sphere to match the measured values of the other two products which are measured as averaged over the Earth's surface. Likewise, to convert the OSWR to the equivalent of the TSI, it needs to be multiplied by 4 in the Albedo equation.
For CERES best product (syn1deg), the values are:
OLWR: 237.2 +/- 10 W/m^2
OSWR: 97.7 +/- 3 W/m^2
Incoming Solar (=TSI/4): 341.3 +/- 0.2 W/m^2
That yields an energy imbalance of 6.4 W/m^2, which contradicts the far more accurately measured energy imbalance from ocean heat content measurements. Knowing the large errors in absolute magnitude of the values, they are therefore adjusted by 27%, 73% and 450% of the 2 sigma error values respectively (for the values shown in the figure shown @159 above). Note that graph is from a slightly different time period from the error values and absolute values I have shown, so that part of the discrepancy may be a difference in the observed values.
The upshot is that the adjustment to the albedo term in the energy budget amounts to approximately 3 W/m^2. HB instead describes it as a greater than 100 W/m^2 fudge. His fudge on the adjustment amounts to a factor of >33. At the same time he describes the OSWR as unobserved which is blatantly false, and neglects that the reason for the fudge is to bring the energy balance into line with observed changes in surface heat content, ie, a decision to use the more accurate determination of the total energy imbalance in preference to one whose inaccuracy due to instrument limitations was an order of magnitude greater. In HB's version of science, scientists should always place greatest weight on their least accurate observations.
I need only add that Trenberth describes the above sources of data, and the reasons for the adjustments at the same place as he mentions them. Given the standard etiquette of quotation and citation, if you are relying on somebody else's word as to what somebody said, you need to quote them rather than the original source. As HB mentions Trenberth directly, he should be assumed to be referencing Trenberth directly, and hence has demonstrated a complete inability to understand the cited source, or a breath taking dishonesty. Perhaps, however, he is as uninformed about the etiquette of citation as he is about climate science, and has merely demonstrated an abominable lack of desire to fact check any factoid he gleans which supports his bizarre theory of what science is.
HB @165.
You dispute the very idea that CO2 in the atmosphere results in an increase in surface temperatures. Yet your use a bowl-of-ice in a-warm-room as an analogy for atmospheric-CO2 above a-warm-surface suggests you are not really thinking through your position. And perhaps you are not entirely clear about what it is you are arguing against. You talk of an absence of “experimental data” to support what you call “the claim that co2 can increase the temperature of the heat source heating it,” this specific to the warming of a surface by the warmed CO2. Yet you go on to suggest that there is after all actually some data but which you consider inadequate, saying:-
What is this "correlation" you mention?
(Note this discussion is not on-topic here and should move to somewhere more appropriate. Indeed, you may even find there your missing “experimental data.”)
168. Tom Curtis
"In fact, the outgoing Short Wave radiation at the Top Of the Atmosphere is measured by the CERES instrument flown on the Terra and Aqua satellites. Together with Total Solar Irradiation (TSI) data from the TIM instrument, that allows the direct calculation of the energy balance and albedo as:
Energy balance = TSI/4 - (OLWR + OSWR)
Albedo = (TSI - 4 x OSWR)/TSI,
where OLWR is Outgoinging Long Wave Radiation, and OSWR is Outgoing Short Wave Radiation."
Then you can provide a reference where we can find an exact definition of albedo? With a description of the included parts and how much they each contribute to reflected radiation?
And how does it relate to the fact that more than 50% of TSI is IR that won´t be reflected?
"The upshot is that the adjustment to the albedo term in the energy budget amounts to approximately 3 W/m^2. HB instead describes it as a greater than 100 W/m^2 fudge."
TSI=1360W/m^2
After albedo=~960W/m^2
More like 400W.
I hope you are aware of that sunlight is much more intense than 340W/m^2?
Do you realise that there is a very large difference between reality where the sun heats the surface at an intensity between 700 and 1000+W/m^2, and your "budget" where you use 340W/m^2?
One is reality and one is your imagination. If the sun only would provide 340W, where is your heat pump connected to an indestructible heat source, that can add energy that isn´t there from the beginning?
I think it is you who need to provide references for your claims about how albedo is an exactly measured factor, with well known and well defined ingredients. While you are at it, provide a reference for the science showing how adding a cold gas to a hot surface can increase the surfacetemperature.
Otherwise you just have a correlation. There are lots of correlations to temperature rising the last century. I claim that increasing obesity in the states is the cause of global warming, it correlates nicely with the temperature. It is as valid as your co2-theory.
MA Rodger at 19:57 PM on 28 December, 2016
HB @165.
"You dispute the very idea that CO2 in the atmosphere results in an increase in surface temperatures. Yet your use a bowl-of-ice in a-warm-room as an analogy for atmospheric-CO2 above a-warm-surface suggests you are not really thinking through your position. And perhaps you are not entirely clear about what it is you are arguing against. You talk of an absence of “experimental data” to support what you call “the claim that co2 can increase the temperature of the heat source heating it,” this specific to the warming of a surface by the warmed CO2. "
I dispute the claim that a cold gas sitting on top of a warm surface heated by a hot star can cause the temperature to rise beyond what the hot star can cause. I dispute the claim that co2 can increase the temperature of its own heat source, especially when it has a mean temperature of -18C in the atmosphere.
I dispute the claim that you can increase the temperature of anything by adding a cold gas, or fraction of a gas, without adding more energy.
I dispute the claim that in the atmosphere, the gasses and water vapor have the opposite effect to what we experience in our daily lives.
Have you ever increased the temperature of anything by adding water vapor that was not pre-heated, or by adding air flowing over it?
I dispute the claim that you have any science to back your claims, aside from hindcasting temperature graphs and showing a doubtful correlation with temperature.
158. MA Rodger at 23:31 PM on 15 December, 2016
"Firstly, the atmosphere is insensitive to up or down. So in addition to radiating 200W/sq m upwards, it also radiates 200W/sq m downwards. It thus requires 400W/sq m to maintain a temperature of theoretically -40ºC (as Stefan-Boltzmann"
Do I understand you correctly?
Are you saying that air at a mean temperature of -18C contains enough energy to radiate 400W/m^2?
To radiate that amount of energy, ignoring the nonsense "photons in all directions", any radiating body has to have a temperature of 289.8K.
It doesn´t matter if it is an atmosphere, it has to have that temperature. Radiating bodys radiate according to their temperature, nothing else.
Where do you find these fairytales?
If your claim is "200W up and 200W down", the atmosphere would have to have a temperature of 243K. You cant add them to get 400W, since you only have one m^2. If your claim is that a cubic meter holds enough energy to radiate 200W in four directions, then you have to explain it much more carefully.
Why do you not divide by four like you do with solar radiation? the same rule applies for cold air as a planet when you treat it as a separate radiating body.
Do you really mean that air chooses to only radiate up and down? How does that work?
HB @171.
Your difficulty seems to stem from an overly simplistic principle you apparently are wedded to - the idea that a cold object cannot warm a hot object. Given such a profound level of misunderstanding, it is best to to simplify the situation by ignoring the external source of heating for the system.
Imagine a hot body (heated magically) and radiating out into space. As space is close to absolute zero, the warm body will receive no energy flux from space, no downward radiation.
Now an atmosphere becomes formed around the hot body which is warmed by the hot body (this atmospheric warming you apparently have no problem with), the atmosphere reaching a chilly -18ºC = 255K at equilibrium. Being warmer than absolute zero, the atmosphere will radiate upward into space and downward back to the hot body. So will the extra energy flux back to the hot body not have a heating effect? Note - if it doesn't we will have to rewrite the laws of thermodynamics and we are not very keen on doing that.
HB @ 172.
If a hot body is flat in form, like an atmosphere surrounding a planet (if you ignore the curvature), it will have a top and a bottom, it will thus have to radiate up and down. Its surface, top and bottom, will be double the surface area of the planet it surrounds. Temperature and surface area dictate the total energy flux. Double the surface and you double the flux. The 400W/sq m was being presented in terms of sq m of the planet beneath, not in sq m of the atmospheric surface which has a top & bottom and thus double the radiation. As you imply in your rather confused final statements, air does not choose a particular direction to radiate to - it radiates in all directions but the sideways stuff has no net flux as that is just the atmosphere heating itself, leaving top and bottom radiation. (By the way, a cube has six sides - (1) top,(2) bottom, (3) left, (4) right, (5) front, (6) back. And the ratio 4:1 to convert discal area (πR2) to spherical area (4πR2) only applies to spheres.)
with refernce to there being a 0.8 deg increase in average global temp since 1880, NASA states, "Two-thirds of the warming has occurred since 1975, at a rate of roughly 0.15-0.20°C per decade".
It's true that the temp has increased by approx 0.53 deg since 1975, which is two thirds of 0.8. However, the temperature had been higher in the 1940's than in 1975, so the reality is just over half the gain has been since the 1940's, not since 1975. Meaning we've had approx 2 x 60 year periods of 0.4 gains.
strop @174,
The quote you cite from the OP is a little out-of-date today and even back when it was written by NASA, it perhaps was niggardly with its "two-thirds ... since 1975." Three-quarters would perhaps have been closer to the mark.
Today the GISS global temperature record is risen another 0.2 deg warmer. Note that the rise 1880s-to-the-1940s was never 0.6 deg (unless you are not talking global). Even cherry-picking a single year the rise to 1944 was 0.47 deg. But a better measure would be 0.3 deg which is just 0.1 deg above a temperature by 1975. (For the record, the cherry-picked 1944 anomaly was bested in 1981.) So today you can say that more than 70% of the warming since the 1880s has occurred since 1980 and less than 30% before 1940 with a dip of 0.1 deg (10%) between 1940 and 1975.