Recent Comments
Prev 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 Next
Comments 14101 to 14150:
-
ChezProvence at 04:01 AM on 24 September 2018Sea level rise is exaggerated
I started at about post #7 with sea level rising at 2.46 mm per year. Eight years later, that may be 3 mm per year (3.46 +/- 0.4) or so ... so about 0.1 in per year ... less than a foot by 2100.
California has accepted a new building code, expecting 10 feet by 2100.
Does this make any sense? Should we all be investing in Dutch dike companies?
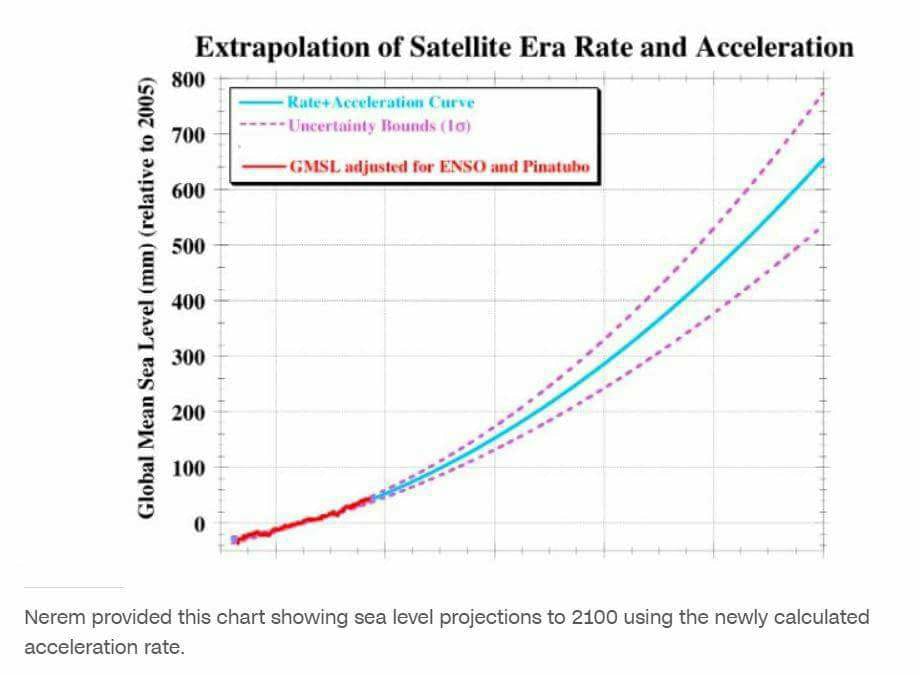
Moderator Response:[DB] And yet, per Nerem et al 2018:
"Global sea level rise is not cruising along at a steady 3 mm per year, it's accelerating a little every year, like a driver merging onto a highway, according to a powerful new assessment led by CIRES Fellow Steve Nerem. He and his colleagues harnessed 25 years of satellite data to calculate that the rate is increasing by about 0.08 mm/year every year—which could mean an annual rate of sea level rise of 10 mm/year, or even more, by 2100."
"This acceleration, driven mainly by accelerated melting in Greenland and Antarctica, has the potential to double the total sea level rise by 2100 as compared to projections that assume a constant rate—to more than 60 cm instead of about 30." said Nerem, who is also a professor of Aerospace Engineering Sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder. "And this is almost certainly a conservative estimate," he added. "Our extrapolation assumes that sea level continues to change in the future as it has over the last 25 years. Given the large changes we are seeing in the ice sheets today, that's not likely."
And:
"the observed acceleration will more than double the amount of sea-level rise by 2100 compared with the current rate of sea-level rise continuing unchanged. This projection of future sea-level rise is based only on the satellite-observed changes over the last 25 y, assuming that sea level changes similarly in the future. If sea level begins changing more rapidly, for example due to rapid changes in ice sheet dynamics, then this simple extrapolation will likely represent a conservative lower bound on future sea-level change."
-
One Planet Only Forever at 02:09 AM on 24 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
John Hartz,
On further reflection I am addressing any marketing efforts.
Advertising and propagada actually have no clear definitions. They can be done to raise awareness or to fool people into wanting or believing something. They can be more understanding/fact-based or more emotional/desire appealing. They can be political or business related. Anyone can believe whatever they want the terms to mean (but Nasi use of the term propaganda definitely still taints perceptions of the term).
My focus is on distinguishing acceptable vs. unacceptable, based on a Governing Objective of improving awareness and understanding and applying that knowledge to develop a sustainable better future for huamnity. And I consider the Sustainable Development Goals and other UN agreements (like nuclear non-proliferation, and Human Rights) to be sub-objectives aligned with that Governing Objective.
It would probably be better to use a term like "promotion efforts" when identifying that the important distinction is how helpful they are, with an added understanding that less factual but helpful promotion efforts are not really OK either. The acceptability is a combination of helpfulness to the development of a sustainable better future for humanity and being based on the improved awareness and understanding that has developed (something sounding helpful but not properly based on the constantly improving awareness and understanding needs to be updated/corrected).
-
One Planet Only Forever at 00:49 AM on 24 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
I would add that I am not really a fan of deliberately misleading messages as part of a government propaganda program, even if the result would be more helpful behaviour of the people influenced by the propaganda.
Early propagada campaigna against Pot in Canada are an example. Discouraging the use of Pot is helpful, especially dicouraging it among younger people, but the campaign was a dismal failure because it was so grossly inaccurate. The new Pot propaganda campaigns in Canada are entertaining appeals for people to not toke and drive, and avoid combining pot with tobacco because of the effects of combined use.
And propaganda is government marketing. Governments do not advertise.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 00:41 AM on 24 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
My definition is the simple use of emotional appeal to popularize a message. And I admit the eveolved concept of the term has been severely tainted by the Nasi use of Propaganda.
So my distinction is that propaganda for harmful intent is unacceptable, especially if the emotional appeal is combined with a deliberately misleading message.
-
John Hartz at 00:10 AM on 24 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
OPF #10: You wrote:
Advertising and propaganda are not a problem. The problem is people being harmfully misleading, especially with appeals built to trigger myopic worldview primal human selfish reactions to overwhelm reasonable thoughtful altruistic modern human consideration.
The second sentence could very well be construed as a description of the "propaganda" process. What is your working definition of "propaganda"?
-
Doug_C at 16:30 PM on 23 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
DrivingBy @6
"Oil is produced because we demand it. Private oil companies exist only because of the world's voracious demand, and if they went 'Poof' tomorrow state owned entities would expand to replace them, albeit with higher overhead.
Most of the world refuses to allow their government to dictate how much energy they consume in the form of food, manufactured products, heated, cooled or humidity controlled homes and asphalt on their roads, and the freight network that hoves all that supports civilization. When we demand these things by buying them, we cause oil to be extracted, transported and refined."
Oil and all fossil fuels aren't being used on a massive level because the public keeps demanding it, they are still the main source of energy for two key reasons.
1. A decadal and massively funded campaign on the part of the fossil fuel sector to deny the inherent risks in using fossil fuels on a massive scale.
2. Huge amounts of money spent to lobby politicians by the fossil fuel sector.
Lets look at British Columbia alone where I am now.
$5.2 million in political donations and more than 22,000 lobbying contacts
In an 8 year period the oil and gas sector paid politicians in BC alone $5.2 million and lobbyed them 22,000 times that's an average of 14 times a day.
These are products that we know are highly dangerous to keep using at the current scale, the only reason we are still on a course to imminent disaster with fossil fuels is because we are being held there firmly by the fossil fuel sector itself which has effectively captured regulators like the Nation Energy Board of Canada.
The courts here have ruled that our national energy regulator is captured by the fossil fuel sector.
After Federal Court quashes Trans Mountain, Rachel Notley pulls out of national climate plan
The majority of people are not asking for disater, we have been removed from the decision making process by those with a fundamental conflict of interest.
-
Doug_C at 16:11 PM on 23 September 2018Video: Textbook Trauma – The Emotional Cost of Climate Change
What's going on with climate change alone is like a diagnosis of a terminal illness... for everyone.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 14:51 PM on 23 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
Advertising and propaganda are not a problem. The problem is people being harmfully misleading, especially with appeals built to trigger myopic worldview primal human selfish reactions to overwhelm reasonable thoughtful altruistic modern human consideration.
And the governing objectives of acceptable leadership action need to be understood to be the promotion of improved awareness and understanding of what is really going on (the latest climate science, or any other learning), and the application of that knowledge to improve and achieve the Sustainable Development Goals.
Without that improved awareness and understanding, a society or organization has no real future. And government advertising and propaganda should be legally required to promote that awareness and understanding - for the good of the future, because the free-market certainly cannot be expected to do it.
-
scaddenp at 12:58 PM on 23 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
One obvious (for William) example would be the NZ Electoral Finance Act 2007 repealed after only two years with a vote 112/9. Nonetheless, NZ does make it more difficult for corporations to buy elections. You can tell if a democracy is in trouble if you have lobbyists talking directly to politicians (buying favours via campaign funding) instead of trying to influence the electorate.
-
John Hartz at 10:55 AM on 22 September 2018California plans to show the world how to meet the Paris climate target
Suggested supplemental readings:
Spotted at the Climate Summit: Republican Mayors by Liz Enochs, City Lab, Sep 19, 2018
Climate Summit Highlights States’ Commitment to Combating Global Warming by Russell Fortmeyer, Architectural Record, Sep 20, 2018
-
MA Rodger at 08:51 AM on 22 September 2018Jennifer Francis: How Climate and Ice Melt Intensify Hurricanes
nigelj @4,
The article you link-to is based on Steffen et al (2018) 'Trajectories of the Earth System in the Anthropocene' which, even with Schellnhuber as a co-author, doesn't provide a list of tipping points projected for +1.5-2.0ºC. The source of the Fyson & Rahmstorf quotes @1 appears to be this web page which does lists five tipping points, referencing a graphic presented within a YouTube video which is Fig 1 from Schellnhuber et al (2016) 'Why the right climate target was agreed in Paris'. This Fig 1 does show thirteen 'tipping points' (if you can call them that), of which five begin to 'tip' below 2.0ºC with one of them entirely 'tipping' below 2.0ºC.
-
nigelj at 05:40 AM on 22 September 2018Jennifer Francis: How Climate and Ice Melt Intensify Hurricanes
Sauerj, the 13 climate tipping points are listed in this article on a useful map.
-
John Hartz at 04:33 AM on 22 September 2018Jennifer Francis: How Climate and Ice Melt Intensify Hurricanes
Recommended supplemetal reading:
How Arctic warming could have steered Hurricane Florence towards the US, Guest Post by Jennifer Francis, Carbon Brief, Sep 17, 2018
-
sauerj at 23:16 PM on 21 September 2018Jennifer Francis: How Climate and Ice Melt Intensify Hurricanes
BBB (@1): Interesting information. Could you reply w/ the list of 13 tipping points, and the 5 that will be tipped at 1.5-2.0C. I would like to see/know that list. Thanks!
-
Lachlan at 16:03 PM on 21 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
William @5, the problem with making it illegal to fund any politician privately is that it entrenches the existing politicians. If nobody has any advertising funding except for the current politicians (or parties), then voting for anyone else would be playing roulette.
I agree that you have identified a big problem, but not with the solution. There is a saying "For every complex problem there is a simple solution, which doesn't work".
-
nigelj at 09:49 AM on 21 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
Driving by @6
Strawman arguments about companies not making oil, dubious comparisons between a single company and entire countries, stating things everyone knows anyway.
In addition, it doesn't matter what exonn does or manufactures, that doesn't absolve them of blame for concealing research on climate change from the public. Nobody is above good ethical standards or consumer law, are they?
Plus omission of obvious facts and cynical lack of balance. We don't have to just "stop using oil" and become hippies :) There are alternatives to not using oil such as renewable energy.
-
DrivingBy at 08:57 AM on 21 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
Oil companies such as Exxon do not create oil, nor are they the great producers. That would be Saudi Arabia, Venezuela, Mexico and the rest of OPEC. The oil companies merely respond to demand by doing the in-between work of buying, transporting, stockpiling and in some cases refining. Some oil is extracted by the major oil componies, but few (none?) equal the scale and output of Saudi Aramco, Pemex or PDVSA. OK, post Chavez PDVSA isn't producing as much oil, but that's not due to any environmental enlightenment. China may well muscle in and flip that condition.
The whole post cleverly tosses aside something more fundamental: Oil is produced because we demand it. Private oil companies exist only because of the world's voracious demand, and if they went 'Poof' tomorrow state owned entities would expand to replace them, albeit with higher overhead.
Most of the world refuses to allow their government to dictate how much energy they consume in the form of food, manufactured products, heated, cooled or humidity controlled homes and asphalt on their roads, and the freight network that hoves all that supports civilization. When we demand these things by buying them, we cause oil to be extracted, transported and refined. To not use oil one drop out of society and exist on animal and hand power.
It would be nice if suddenly the world's population decided to do as we see fit and not use products, services or forms of energy produced by fossil fuel. People say they would like to do so, but almost no one outside people reading sites like this (maybe 0.5% of the world, if that) will follow up.
When there's a demand for a product or service, a few people or nations notice and find a way to fulfill that demand. Blaming the providers for doing so implies that you are somehow entitled to direct what people want and what they may exchange their time and toil for. Both the consumers and those who would be the supply to their demand will dissent, and vigorously.
Moderator Response:[DB] Sloganeering snipped.
-
BeezelyBillyBub at 08:27 AM on 21 September 2018Jennifer Francis: How Climate and Ice Melt Intensify Hurricanes
We must reduce emissions 50% in 10 years to avoid 1.5° C. | Claire Fyson
1.5° due by 2030.
We must reduce emissions 100% in 20 years to avoid 2° C. | Stefan Rahmstorf
2 C° due by 2050.
2° C = DISASTER | James Hansen
1° C = DANGEROUS CLIMATE CHANGE | James Hansen
5 of 13 Tipping Points start at 1.5° - 2° C = Cascading Runaway Heating. | Hans Schellnhuber
Moderator Response:[DB] All caps usage snipped.
-
william5331 at 05:33 AM on 21 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
Big companies are amoral. Nothing new here. This applies even to the Pharacutical companies that do give us many life saving products. They also hide negative results of their research as has been revealed many times. The argument by the fuel companies that it is the responsibility of governments to take the necessary measures to protect their people is well taken but the last estimate I have heard, is that there are at least a hundred lobyists in Washington for every politician and the big companies and rich individuals finance political elections. Who pays the piper calls the tune. Until politicians are financed from the exchequer and it is illegal for any person or company to give money for any reason what so ever to a politician, we can forget about them representing us.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 01:14 AM on 21 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
I do not have a problem with some people being wealthier than others.
People who have been more helpful regarding the improvement of awareness and understanding of what is really going on and the application of that learning to help develop a sustainable better future for humanity should be more highly regarded and rewarded than others.
The obvious problem is that those type of people are at a competitive disadvantage. People with other interests can easily become bigger winners than they deserve to be, especially when they can abuse the awareness and understanding of the power of misleading marketing to easily tempt people to have a more limited, more myopic, worldview.
Trying to be a winner in ways that are harmful to the future of humanity needs to be treated like current day harmful pursuits of personal perceptions of superiority relative to others. Those actions are discouraged and penalized. We are starting to see that correction occurring. But there is lots of resistance to those corrections by undeserving wealthy and powerful people, especially in supposedly 'more advanced nations', nations, regions, corporations and communities that have only developed unjustified perceptions of superiority relative to others.
For societies and organizations to be truly sustainable, they need to develop higher expectations for helpful behaviour by 'their winners and leaders', and correct or penalize the ones who are 'less deserving of their developed perceptions of superiority'.
Achieving the corrections identified by climate science requires improved awareness and understanding of more than climate science.
-
Philippe Chantreau at 23:39 PM on 20 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
No that many people Jef. Compared to the whole of humanity, very few, in fact.
-
jef12506 at 10:55 AM on 20 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
Yes but a lot of people got rediculously rich in the process so that makes it ok.
-
John Hartz at 07:25 AM on 20 September 2018California plans to show the world how to meet the Paris climate target
Recommended supplemental reading:
Jerry Brown Made Climate Change His Issue. Now, He’s Not Sure How Much Politicians Can Do. by Somini Sengupta, Climate, New York Times, Sep 18, 2018
-
One Planet Only Forever at 05:40 AM on 20 September 2018Shell and Exxon's secret 1980s climate change warnings
The 1987 UN Report "Our Common Future" included the following stetment making it undeniable what the 'winners/leaders' of the time had been doing:
"25. Many present efforts to guard and maintain human progress, to meet human needs, and to realize human ambitions are simply unsustainable - in both the rich and poor nations. They draw too heavily, too quickly, on already overdrawn environmental resource accounts to be affordable far into the future without bankrupting those accounts. They may show profit on the balance sheets of our generation, but our children will inherit the losses. We borrow environmental capital from future generations with no intention or prospect of repaying. They may damn us for our spendthrift ways, but they can never collect on our debt to them. We act as we do because we can get away with it: future generations do not vote; they have no political or financial power; they cannot challenge our decisions.
26. But the results of the present profligacy are rapidly closing the options for future generations. Most of today's decision makers will be dead before the planet feels; the heavier effects of acid precipitation, global warming, ozone depletion, or widespread desertification and species loss. Most of the young voters of today will still be alive. In the Commission's hearings it was the young, those who have the most to lose, who were the harshest critics of the planet's present management."And the success of the fossil fuel industry is the expected result of nations failing to improve the awareness and understanding of their populations. That failure develops myopic worldviews, people caring more about near-term benefits for a small portion of current humanity, caring less about others or longer term interests like the future of humanity.
And how much better are the Winners/Leaders today ---> many are more aggressively regressive.
That failure to responsibly lead the improvement of awareness and understanding, failure to improve and expand worldviews to the future of all of humanity, is exactly what John Stuart Mills warned about in "On Liberty" when he was discussing the ability of the elites (winners) in a society to responsibly educate all members of their society. He stated "If society lets a considerable number of its members grow up mere children, incapable of being acted on by rational consideration of distant motives, society has itself to blame for the consequences."
Societies around the planet have not only failed to be led to improved awareness and understanding, many are developing winners who more aggressively fight against the population developing improved awareness and understanding - and they are still able to get away with it.
In spite of how undeniably harmful to the future of humanity the deliberate misleading of the public regarding climate science actually is, I cannot name a politician who has been brought to trial for deliberately misleading the public regarding climate science, or one that has even just been declared incapable of responsibly performing the duties of their esteemed elected high-office position and been removed from office without having to wait for 'the next election'.
-
ubrew12 at 04:28 AM on 20 September 2018Video: Textbook Trauma – The Emotional Cost of Climate Change
When the social contract is broken by those in power, the reaction by those out of power is dissociation. Society falls apart. Large parts of society are no longer engaged in it: they've opted out and have drugs, television, video games. I used to feel rage toward people like the Koch Brothers funding a lie that will hurt the Earth and probably kill millions of people. Now I just feel numb. Everything we were taught as children about the rightness of America has been a lie, currently epitomized by the sitting President.
-
One Planet Only Forever at 02:55 AM on 20 September 2018California plans to show the world how to meet the Paris climate target
The following is to reinforce the point in my comment@2 that charitable (or helpful) behavior by a portion of the population will not be enough to solve a problem that has been created by the developed socioeconomic systems.
Imagine if the corrections of what was being done to Lake Erie, the River Thames, or the ozone layer only happened through the choices made by the consuming public:
- with corporations able to keep the general population from becoming more aware of what they were actually doing to produce the things people were buying, claiming things like corporate privacy rights.
- without any actions by people external to the marketplace trying to improve awareness and understanding of what was going on.
- with little restriction on misleading marketing tempting people to 'desire' things without understanding the real implications of consuming what they have been tempted to desire.
There would have been no meaningful corrections without parties external to the marketplace improving awareness and understanding and being able to Impose restrictions and limits on the damaging unsustainable activities.
And regarding the overall actions of California leadership. Are they also going to eliminate the unsustainable rate of removal of water from aquifers that is fueling their unsustainable agriculture operations? Are they going to end the 'grandfather permissions' for old dirtier fossil fuel activity to continue to operate uncorrected?
-
Alexandre at 22:17 PM on 19 September 2018California plans to show the world how to meet the Paris climate target
BeezelyBilly, maybe you would consider adding this graph to your collection?
-
Alexandre at 22:03 PM on 19 September 2018Video: Textbook Trauma – The Emotional Cost of Climate Change
This emotional part is huge. We care a lot about the environment, we know this is important to our well being way before we do the math. Even those anti-environmentalists think bad news about the environment are depressing. Even those guys care. A while ago I (unsuccessfully) tried to write something about how this should be harnessed to mobilize people for mitigation - we just love nature, and it's just too sad to see what's happening. It's great to have the science to back you up, but sometimes I feel as if the details of all those scientific papers make us miss the big picture of what's happening. Maybe it's another way of seeking safety?
-
BeezelyBillyBub at 19:44 PM on 19 September 2018California plans to show the world how to meet the Paris climate target
In 20 years 80% of all cars will be gas or diesel. Get real.
Here are all the climate/energy charts you need in one spot.
https://lokisrevengeblog.wordpress.com/2018/05/28/charting-collapse/
Moderator Response:[JH] Sloganeering snipped. Argumentative snide remark snipped.
Please note that posting comments here at SkS is a privilege, not a right. This privilege can be rescinded if the posting individual treats adherence to the Comments Policy as optional, rather than the mandatory condition of participating in this online forum.
Please take the time to review the policy and ensure future comments are in full compliance with it. Thanks for your understanding and compliance in this matter.
-
BeezelyBillyBub at 19:30 PM on 19 September 2018California plans to show the world how to meet the Paris climate target
2° C = DISASTER | James Hansen
1° C = DANGEROUS CLIMATE CHANGE | James Hansen
5 of 13 Tipping Points start at 1.5° – 2° C = Cascading Runaway Heating. | Hans Schellnhuber
The latest permafrost wetlands study show those emissions are newly considered a tipping point, which means the Paris climate budget is outdated.
WHAT THIS MEANS IS WE HAVE A 66% CHANCE OF HITTING DISASTER
A 44% CHANCE OF HITTING SOMETHING WORSE THAN DISASTER.
Moderator Response:[DB] All-Caps usage stricken, per the Comments Policy.
"Cascading Runaway Heating"
Unlike the simple example of positive feedback we learned in high school, the increase from every round of feedback gets smaller and smaller, in the case of the enhanced greenhouse effect. It is a significant factor in the overall warming, but it does NOT lead to a "runaway" trajectory for temperature. Place any further remarks on that topic at that thread, please, and not here.
-
nigelj at 07:08 AM on 19 September 2018Video: Textbook Trauma – The Emotional Cost of Climate Change
Yes some problems like climate change create serious dangers for humanity, which naturally leads to fear, anger and guilt. This is how humans are constructed, and its utterly normal. It's to impel us to make a response, because it creates a state of worry and tension that is very uncomfortable, and this can only be resolved by making a decision. Psychology 101.
Some people make the decision that we need action to reduce emissions, some people decide there is no problem (denial), some seek to rationalise the problem away. There are almost infinite ridiculous, flawed ways of rationalising the problem away.
-
swampfoxh at 03:26 AM on 19 September 2018California plans to show the world how to meet the Paris climate target
I think the true impact of Animal Agriculture is closer to 50% of global emissions when you account for desertification, deforestation, eutrophication and acidification of the oceans, wild animal habitat loss, the raising of massive animal feed products and fresh water use by Animal Ag. Seems to me that California isn't dealing with these issues and other external costs associated with Animal Ag. Does anyone tracking along with skepticalscience.com have a scientifically defensible number for Animal Ag's contribution to GGEs? Is California's 18% defensible?
Moderator Response:[DB] Please take all discussion of Animal Agriculture to this thread. Thanks.
Off-topic snipped. Any responses should be placed at the link, not here. -
One Planet Only Forever at 02:42 AM on 19 September 2018California plans to show the world how to meet the Paris climate target
Helpful Leadership examples are important.
A more important development would be effective penalties for 'supposed winners/leaders' who act in harmful/unhelpful ways. A particularly important development would be legal penalties for anyone who can be shown to be developing or disseminating misleading marketing that would create unjustified popular support for undeserving smaller worldview private interests (interests of a sub-set of humanity in a shorter time-frame - their personal desires in their lifetime), interests that are contrary to achieving the larger worldview public interests of the Sustainable Development Goals (all of humanity now and into the distant future). And the expectations of helpfulness should be more strictly enforced the higher the status of the person behaving questionably (higher status, wealth or influence in business or politics).
Ultimately, achieving good results requires everyone who genuinely wants to be helpful to be able to restrict and correct the harmful unsustainable developments that can be encouraged and defended in competitions to appear to be superior to others, especially when acceptability is judged by measures of profitability or popularity. As examples, the damage done to Lake Erie, the River Thames, or the ozone layer, was not rapidly corrected by the people who benefited from the damage done self-correcting their behaviour based on thoroughly and carefully improving their awareness and understanding of the impacts of their activity. In fact, there are always delays in curtailing the harmful activity. Others usually identify the unacceptability of the behaviour. And the damage done is never fully corrected. And the ones who benefited most from the damage done are very rarely the ones who end up cleaning up the results of the damaging unsustainable actions they benefited from.
The required development and corrections, like achieving the Sustainable Development Goals, cannot be expected to be accomplished by charitable actions of a portion of the population, especially if others remain freer to continue to try to benefit by making a bigger problem for the charitable to try to overcome. Misleading marketing that tempts people to desire a smaller worldview is harmful, and should be effectively penalized to discourage it.
The Dance of development by the freer actions of people is predictable. It can be easily understood to motivate the development of fundamentally unsustainable and harmful behaviour. Predictable results are produced when 'pursuit of primitive human desires for impressions of superiority relative to others (small worldview)' are not effectively limited by the 'modern human ability to compassionately and thoughtfully pursue improved awareness and understanding to help develop a sustainable better future for humanity (larger worldview)':
- Harmful unsustainable activities are easier to benefit from, making them more tempting and potentially easy to make more popular.
- People getting away with behaving less acceptably have a competitive advantage compared to others who care more and self-limit their behaviour more responsibly.
- As more people see examples of others winning by getting away with harmful unsustainable behaviour, more people can be expected to choose to behave more barbarically less acceptably.
- The beneficiaries of the less acceptable behaviour seldom willingly self-correct their behaviour. Correcting the harmful developments of that competition often requires external restrictions imposed on the freer competition that developed the more barbaric problem behaviour.
The future of humanity clearly requires improved awareness and understanding of what is going on. It needs Helpful Altruistic (large worldview) people to be able to effectively govern and limit the behaviour of harmful (small worldview) people as the helpful also try to educate the entire population in order to reduce the number of people who require external governance, reducing the need for 'bigger government'.
I am sort of a reverse-Conservative. I like the idea of smaller government. But I do not support the belief that smaller government will develop a better society. I understand the need for the general population to be better educated, including corrections, in order to reduce the need for larger government. A better-informed and more considerate population is required to make freer Political and Economic Democracies successful (sustainable).
-
michael sweet at 23:04 PM on 18 September 2018New paper shows that renewables can supply 100% of all energy (not just electricity)
Geotim,
Many analysis indicate that there is much more than enough renewable energy to power the netire world. There are ongoing discussions about the best way to store power to use during periods of high demand with low wind and sun. The OP describes Jacobson's plan which uses hydrogen as primary storage. Other plans (Connolly) use methane or methanol as primary energy storage.
Jacobson's plan has been criticized as using too much hydropower. Connolly's plan would use existing methane peaker plants to supply backup (much of the methane could be stored in existing facilities).
One thing I can tell you for sure: the energy system is very complicated and difficult to understand.
According to both of these plans, renewable energy will cost less than fossil energy. In addition, renewable energy will result in dramatically reduced pollution. Lower pollution will mean less disease and early death. If you add the health savings to the energy cost it is a tremendous cost savings. Of course, the recent Trump energy plan assigns a zero value to human lives lost.
Think it through: if renewable energy cannot supply enough power for the entire world, what will people do in 100 years after all the fossil fuels are used up? Do you think they will all go live in caves? Everyone expects future people to solve this problem.
-
RedBaron at 10:43 AM on 18 September 20182018 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #37
Michael,
You can get ongoing trials results from several places, but the easiest is Rodales 30 years+ study. They added no till organic to the traditional organic methods a few years back. Yearly updates from them are available. But the best thing anyone can do is stop growing too much corn in the first place. Turn those cornfields back into prairies and graze them directly. That's the ticket to the very best of the best results, because it turns a major emissions source into a major sequestration sink.
-
Eclectic at 10:20 AM on 18 September 2018Does breathing contribute to CO2 buildup in the atmosphere?
GeoTim @71 , you are now wandering way off-topic for this thread.
Please find one of the many threads discussing the replacement of fossil carbon fuels by "zero-carbon" energy sources, and express your well-considered thoughts there. The change-over to "zero nett carbon" could be achieved in around 20 years using present-day technology — let alone the likely more efficient solar technology which will be under development currently. "Nuclear" is also possible, but is very slow to construct, and is very expensive (see the impressively large subsidy donated by RossAtom to the Finland economy for the new reactors there).
Considering that most present-day coal/gas electricity generation stations will be expiring of old age in 20 or so years (and most of today's cars and trucks will also "age out") . . . it turns out that it is little or no additional cost to replace them with zero-carbon machinery.
The main exception is airplanes and ships — they can use kerosene/diesel made by vat fermentation ~ but this technology is not yet in large-scale economic production. But likely will be reasonably cheap in 20 or 30 years' time.
Additional threads can be found that discuss reducing atmospheric CO2 by returning carbon to the soil (soil micro-organisms can sequester large amounts of carbon compounds, with better farming/grazing management methods).
Moderator Response:[PS] Indeed offtopic. Please move any further response to this thread.
-
RedBaron at 08:56 AM on 18 September 20182018 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #37
Michael,
The idea is to end subsidies causing AGW like corn, and instead reward carbon sequestration. Those corporate farms would either need to hire a whole lot of people, or break up their farms, because as a rule they are far too large to optimally sequester carbon. The smaller 100-300 acre farms would have a huge advantage here. Those huge corporate farms are actually net carbon emissions sources and likely would be taxed right along with the fossil fuel companies. Ag is number two in net emissions.
-
GeoTim at 08:04 AM on 18 September 2018Does breathing contribute to CO2 buildup in the atmosphere?
With all due respect, may I ask whether we have the capacity to provide the needed energy using renewables or nuclear power if fossil fuels were gradually terminated? The objective, of course, would be to reduce the amount of CO2 generated each day (including humans') to a level that can be consumed by current and future consumers (photosynthesizing plants, coral, and ocean water, etc.) and not adversely effect the biosphere; in other words to a sustainable level. I do not fill energetic enough (and I make mistakes) so I will take the suggestion to not perform any more calculations and leave you with the idea of sustainability. I would love to read the plan someday.
-
spartimus at 08:00 AM on 18 September 2018Ocean acidification isn't serious
forgive my foolishness, meant carbonic acid, not carbolic acid
-
spartimus at 07:56 AM on 18 September 2018Ocean acidification isn't serious
I am a 1st year biology student who dreams of becoming an expert in plant biology and organic chemistry at some far off point in the future. First off, I want to thank everyone here for the nuanced and intelligent level of discussion. In reading both the article, and the ensuing discussion posts, I have 2 questions that are probably answered by previous posters but am hoping that you may take time to help me understand more deeply. With increased CO2 in oceans and the ensuing rise in carbolic acid and reduction in the aragonite in the water, how much more energy does it take for coral and plankton to create their exoskeletons? Second question, and this may be stupid, but after past mass coral die offs, how long did it usually take for a rebound or regrowth of coral based on fossil records?
Thank you all again for the lively and intelligent debate despite the fact that at this point, most of this information went over my head. I plan on reading as much as I can on this topic since currently we are learning about chemical reactions in water and also about formation and modification of biological molecules and I find this topic extremely fascinating and also extremely scary and am really interested in gaining a more informed and nuanced understanding of these topics.
Cheers
-
John Hartz at 07:36 AM on 18 September 2018California plans to show the world how to meet the Paris climate target
Recommended supplemental reading,,,
California Had Its Own Climate Summit. Now What? by Brad Plumer, Climate, New York Times, Sep 15, 2018
-
michael sweet at 07:09 AM on 18 September 20182018 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #37
Nigelj,
While I could imagine a system that might be better than universal dividend, I think the systems you propose are too complicated for most Americans to think the government could implement them fairly. A 100% dividend is simple and could be easily audited. It is easy for people to understand where the money is going.
The amount must be high enough to affect the cost of carbon. $10 per ton is too low to affect price significantly. If a steadily increasing fee, starting at $10 and going up at $10 per year would eliminate carbon pollution in 15 or 30 years. The low start would give people time to adjust so the economy would not be shocked.
Assessing the affects of a $10 fee is a waste of time since it is too small to have a significant effect.
-
michael sweet at 07:02 AM on 18 September 20182018 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #37
Red Baron,
I am glad we agree that most of the land is in large corporate farms. That would mean that any program that rewarded farmers on a per acre/per pound carbon sequestered would go primarily to large corporations. Those operations are already heavily subsidized in the USA (for only one example, the entire ethanol in fuel program is a subsidy for corn farmers).
I would vote against any program where the money went primarily to large commercial farmers.
Your new citation is from 2002. Can you cite anything recent (past 5 years perferably) to support your claim "results keep coming in consistantly overturning that antiquated notion." Citations should be peer reviewed and not newspaper reports. In general, I have found your references to poorly support your claims. I do not like to argue against any possible solution to the carbon crisis, but when you use these claims to counter another possible solution you must support your claims.
-
nigelj at 06:03 AM on 18 September 20182018 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #37
According to this article: "Lumping in farms with sales of over $250,000 a year, and these so called large-scale commercial farms represent just 10% of the country's farms but account for 82% of its overall food production."
This suggests to me that the majority of the land is owned by commercial operations with good incomes.
However I dont think its a question of farm incomes as such. While I dont believe in throwing arbitrary subsidies at wealthy farmers, a subsidy for improving soil carbon would be more specific. It would require intensive monitoring to make sure the required work is being carried out.
This leaves the question of how to fund such a subsidy. The problem is using the carbon tax income as a subsidy for farming would be competing with other possible subsidies such as wind power in a long list of competing interests. You would probably end up with political grid lock on the issue in America, and as M Sweet says it could be seen as government over reach.
It's probably better in political terms that a carbon tax and dividend be kept simple with all the dividend given back to people. I personally like subsidies, but I accept they are probably not going to work as part of a carbon tax in america.
It might be better to subsidise farming soil programmes out of the states general tax revenue. Then there are less arguments about federal government over reach.
The other alternative would be to reduce the carbon tax itself for farms that farm sustainably with soil carbon programmes. This would encourage farms to move in this direction.
-
RedBaron at 05:26 AM on 18 September 20182018 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #37
@Michael Sweet,
You are correct that this strategy was thought impossible even 20 years ago, and highly unlikely even 10 years ago, but results keep coming in consistantly overturning that antiquated notion.
Please remember that even as recently as 1996 we had no idea about this entire new carbon pathway into the soil even existed!
Glomalin eluded detection until 1996 because, “It requires an unusual effort to dislodge glomalin for study: a bath in citrate combined with heating at 250 F (121 C) for at least an hour.... No other soil glue found to date required anything as drastic as this.” - Sara Wright.
Let that sink in a bit. An entire pathway that sequesters carbon directly into the soil by plants once thought to be less effective at carbon sequestration, but actually now we are finding are 10 times MORE effective at long term carbon sequestration than even the most productive tropical rain forests!
The soil sink is far larger than both all the atmospheric Carbon and terrestrial biomass carbon combined. Yet one quarter to one third of that soil sink carbon was completely unknown prior to 1996.
Glomalin: Hiding Place for a Third of the World's Stored Soil CarbonAs far as the size of farms in the US goes, the average is 300 acres, but that includes a lot of small hobby farms and truck farms that usually requires an outside job off farm to avoid bankruptcy.
The USDA published an optimum size farm to be profitable if using standard BMP (best management practices) on commodities and found the minimum starting acreage capable of supporting 1 family was 2000 acres. That article was moved and I never found its new location at the USDA, but it seems to suggest that both of you are partly correct. Most the acreage is in large commercial corporate farms, while most the farms are still small family run operations. (which are still failing at an alarming rate)
-
michael sweet at 22:23 PM on 17 September 20182018 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #37
PS:
According to your data, there are approximately 2,100,000 farms in the US. The average sales of all farms farms is $190,000. There are about 480,000 with sales over $100,000 but I estimate only about 350,000 (17% of all farms) of those have sales over $190,000. Less than 20% of farms have sales over the average ($190,000). About 160,000 (7.6%) have sales over $1 million. The farms wiith high sales would have a disproportionate amount of the land farmed. Most farms with $190,000 in income would have low profit after mortgage payments and other costs.
About 1,400,000 (70%) of the farms have less than $25,000 in sales and are hobby farms or deliberate loss farms for tax purposes. I live on a farm that had sales over $25,000 this year for the first time. We paid the entire mortgage from the farm for the first time.
I stand by my claim that "the great majority of land farmed is owned by large corporations or multimillionaires."
Moderator Response:[PS] I remain unconvinced. According to this, non-family farms account for 3% of farms, 15% of production
-
michael sweet at 09:07 AM on 17 September 20182018 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #37
Red Baron:
From the abstract of your first reference:
"Most scientists contend carbon is a useful factor to consider
for agronomy but not for sequestration." (my emphasis)The second article is about the same scientist the first article was written about. (They are both ten years old. By now they should have results you could cite). Your references state that most scientists do not think your proposals will work.
The point of tax and dividend is that it does not increase the size of government since all the fee is paid out as dividends. Many conservatives in the US will not vote for anything that increases the size of government.
Your proposal to redistribute the fee to rich farming corporations would never fly. (Please do not come back with the argument that farmers are all poor families. In the USA the great majority of land farmed is owned by large corporations or multimillionaires.)
Moderator Response:[PS] "great majority of land farmed is owned.." it would be good to have a cite for this. US Census data for instance does not appear to support that assertion.
-
RedBaron at 08:35 AM on 17 September 20182018 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #37
I have to dissagree here. That sort of carbon tax and dividend is unworkable.
I could see a carbon tax as a possibility, but certainly not as a goody trick or treat bag back to everyone. That's like rearranging the deck chairs on the sinking Titanic. It's like Carbon Welfare payments. ARRRG. Since when did welfare ever eliminate poverty? But it is somehow going to eliminate global warming? Really?
If you are going to tax carbon, then the ONLY possible purpose for that money is to fund those sequestering carbon out of the atmosphere. Then at least the tax is funding a public works project.
This whole wealth distribution meme is getting as tiresome as it is impossible to fix anything.
You must have a very clear purpose for the tax. It is to fund verified CO2 sequestration. You must have a clear price for CO2. So as soon as you get verification of sequestered carbon, then that money determines the carbon payment being collected by a tax.
The tax of course will be small first years because most people are not sequestering carbon. But over time as more and more people sequester carbon, the tax will rise since the set price per ton sequestered is fixed.
People will get better and better at sequestering carbon, because they get paid by the ton for doing it. The biggest gain is of course for farmers, since at least 5-20 tonnes CO2e / ha /yr can be sequestered long term in the largest terrestrial sink on the planet... the soil.
Liquid carbon
pathway
unrecognisedThey started a similar strategy in Australia, but canceled the program because people figured out it would most certainly work. It scared the fossil fuel industry how easy and effective this strategy is. Massive funding by fossil fuels reversed the political power in the elections.
FARMING A
CLIMATE CHANGE SOLUTIONLets say we put a price of $50.00 a tonne. Then soil samples can be taken. and if the deep carbon content of the soil is increasing, then the payment of $250.00 to $1000.00 per acre of farmland would make an amazing difference for the cost of the food that farmer produces.
Be sure the farmers would pile on that goldmine like crazy and the US carbon footprint would go negative rapidly as fossil fuels scrambles to get into solar wind and hydroelectric and farmers put massive quantities of carbon back in the soil where it belongs. Once more carbon is being sequestered than produced, it actually collapses the few remaining fossil fuel producers unless they are protected by offsets sequestering their footprint like CCS or other ways people sequester carbon.
I actually think it is workable without a carbon tax. Just stop taxing and spending on those things causing AGW should be enough. But if not, then at least be straight forward results orientated with the tax and spend. Use it to fund CO2 drawdown!
This kind of petty government bribery you propose by dividending everyone ie voting ourselves a check, is ridiculous and NEVER worked in the past. What makes you think it could even have a chance of working this time?
Geeze, no wonder the Republicans are fighting you guys tooth and nail. Insanity.
Moderator Response:[DB] Inflammatory and ideology snipped.
-
nigelj at 08:29 AM on 17 September 20182018 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #37
Humans prolific consumption patterns are having serious environmental impacts that are now obvious and well documented. Much of this is driven by over consumption beyond basic physical needs, driven by status seeking and a need to compete and win - which is part of our human nature. I'm as guilty of this as anyone.
Human nature is not a simple thing to change, or even a desirable thing to change at a fundamental level, because competition can create great things. What we need to do instead is direct our human nature in positive ways:
1) we need stronger laws to stop the impacts on the environment.
2) leaders need to set a good example. Society works on the basis of leadership. Power and money is a privilege. It is not a licence to hoard resources or dodge reasonable laws.
2) we need a carbon tax and dividend that gives a clear price signal that fossil fuels are a problem. There are other more brutal ways of cutting off the supply but carbon tax and dividend is practical and politically plausible.
3) we need to educate kids that there are other ways of living a good life, and demonstrating success and self worth other than living in a huge mansion or owning the largest car. It's size that has some of the largest environmental impacts for obvious reasons although high tech can also have significant issues. If we don't, the planet will do the educating the hard way with severely altered climate and severely depleted and poisoned resources.
-
BeezelyBillyBub at 08:22 AM on 17 September 2018New research, September 3-9, 2018
Humanity has never had a 100% energy transition. We still burn wood.
Europe gets 50% of its renewable enery burning wood, and do not count the emissions because the trees will grow back in 50 years.
If world energy demand got 2% more of its energy from wood, we would need 100% more timber harvested.
Stefan Rahmstorf says we must reduce emissions 100% in 20 years to avoid 2 C.
Claire Fiore says we must reduce emissions 50% in 10 years to avoid 1.5 C.
Vaclav Smil says a 100% energy transition takes 70 years, if at all.
James Hansen says 2 C = DISASTER, 1 C = Dangerous Climate Change.
We are already at +1 C.
Permafrost wetlands are turning from carbon banks into carbon bombs and threaten to double emissions. This is not modelled.
Rainforests and soils are turning from carbon banks into carbon bombs.
Greenland freshwater runoff has only just very recently included in models.
Fracking emits 4X more methane than reported and threatens to advance the 2 C tipping point.
Five tipping points are triggered between 1.5 - 2 C and threaten cascading collapse as do dominos.
In 10 years freshwater demand will exceed supply by 30%.
We lost 30% of our soil in the last 40 years.
By 2020, 66% of animals will be gone.
Humans and Livestock make 97% of land vertebrate biomass.
10,000 years ago H&L were 0.03% of land vertebrate biomass.
We will run out of food and water before we ever transition to 100% renewable energy.
This is because electricity production is only 20% of total world energy demand.
https://lokisrevengeblog.wordpress.com/2018/08/03/34355/
Prev 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 Next































 Arguments
Arguments