 Arguments
Arguments
 Software
Software
 Resources
Comments
Resources
Comments
 The Consensus Project
The Consensus Project
 Translations
Translations
 About
Support
About
Support


Latest Posts
- Two-part webinar about the scientific consensus on human-caused global warming
- Sabin 33 #22 - How does waste from wind turbines compare to waste from fossil fuel use?
- Clean energy generates major economic benefits, especially in red states
- 2025 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #13
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #13 2025
- Climate skeptics have new favorite graph; it shows the opposite of what they claim
- Sabin 33 #21 - How does production of wind turbine components compare with burning fossil fuels?
- China will need 10,000GW of wind and solar by 2060
- 2025 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #12
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #12 2025
- Climate Fresk - a neat way to make the complexity of climate change less puzzling
- Sabin 33 #20 - Is offshore wind development harmful to whales and other marine life?
- Do Americans really want urban sprawl?
- 2025 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #11
- Fact brief - Is waste heat from industrial activity the reason the planet is warming?
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #11 2025
- Visualizing daily global temperatures
- Sabin 33 #19 - Are wind turbines a major threat to wildlife?
- The National Hurricane Center set an all-time record for forecast accuracy in 2024
- 2025 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #10
- Fact brief - Is Greenland losing land ice?
- The Cranky Uncle game can now be played in 16 languages!
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #10 2025
- Climate Adam: Protecting our Planet from President Trump
- Sabin 33 #18 - Can shadow flicker from wind turbines trigger seizures in people with epilepsy?
- Cuts to U.S. weather and climate research could put public safety at risk
- 2025 SkS Weekly Climate Change & Global Warming News Roundup #09
- Fact brief - Are high CO2 levels harmless because they also occurred in the past?
- Skeptical Science New Research for Week #9 2025
- Is CO2 plant food? Why are we still talking about this?
Foster and Rahmstorf All
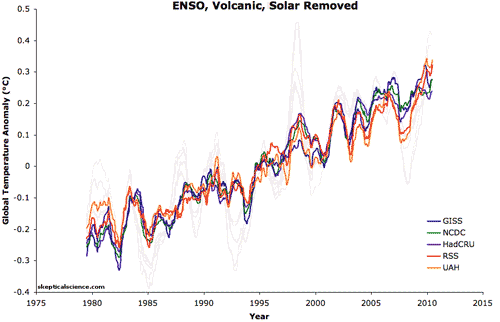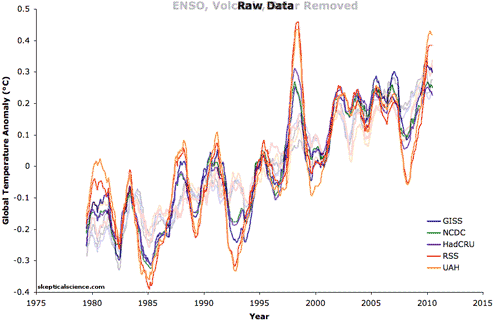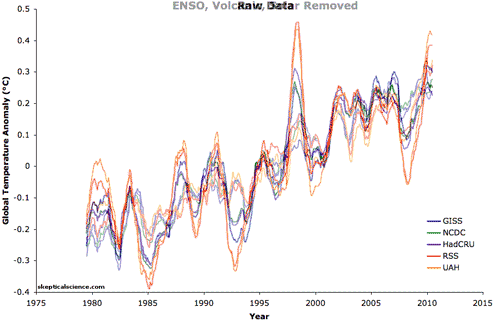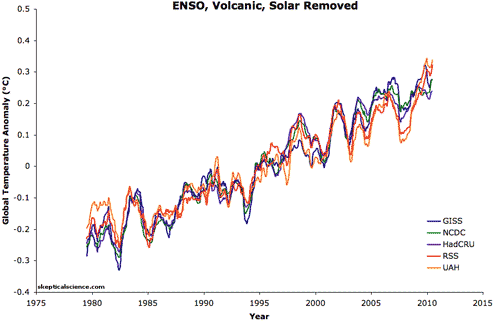
Five datasets of global surface temperature and lower troposphere temperature are shown in this animation before and after removing the short-term effects of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), solar variability, and volcanic aerosols. A 12-month running average was applied to each dataset. Foster and Rahmstorf (2011) used multiple linear regression to determine and then statistically filter out these short-term effects to reveal the steady underlying trend of primarily human-caused global surface warming. This method effectively removes the short-term noise that can complicate the interpretation of temperature trends or permit "cherry picking" of graph endpoints or short time periods to find periods that erroneously suggest global warming has paused rather than continued unabated as these results show.
SkS Resources that use this Graphic
- Foster and Rahmstorf Measure the Global Warming Signal
- The Big Picture
- Updating the Climate Big Picture
- Rahmstorf et al. Validate IPCC Temperature Projections, Find Sea Level Rise Underestimated
- UAH Misrepresentation Anniversary, Part 2 - Of Cherries and Volcanoes
- Did Global Warming Stop in 1998, 1995, 2002, 2007, 2010?
- Global Cooling - Is Global Warming Still Happening?
- Solar Activity & Climate: Is the Sun Causing Global warming?
- How Do Volcanoes Drive Climate?
- Global Warming and the El Niño Southern Oscillation
- What Has Global Warming Done Since 1998?
- Roy Spencer's Junk Science
- Global Surface Warming Since 1995
- Rose and Curry Double Down on Global Warming Denial
- Climate of Doubt Shines a Light on the Climate Denial Movement
Images
Printable Version | Back to Graphics by Skeptical Science
|
|
Skeptical Science Graphics by Skeptical Science is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. |
THE ESCALATOR

(free to republish)
























































