NASA: Climate Change May Bring Big Ecosystem Changes
Posted on 18 December 2011 by John Hartz
This article is a reprint of a news release posted by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Dec 14, 2011.
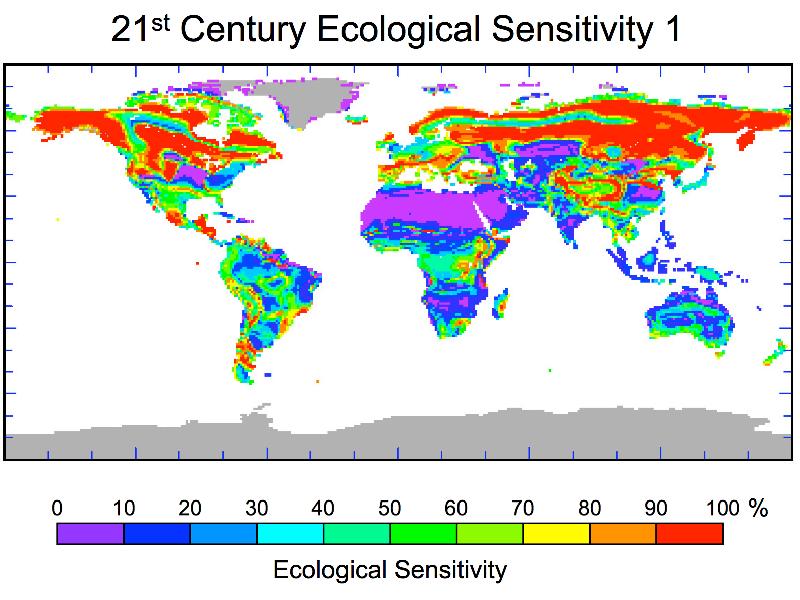
Figure 1: 21st Century Ecological Sensitivity - Changes in Plant Species
Predicted percentage of ecological landscape being driven toward changes in plant species as a result of projected human-induced climate change by 2100.
By 2100, global climate change will modify plant communities covering almost half of Earth's land surface and will drive the conversion of nearly 40 percent of land-based ecosystems from one major ecological community type - such as forest, grassland or tundra - toward another, according to a new NASA and university computer modeling study.
Researchers from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, Calif., investigated how Earth's plant life is likely to react over the next three centuries as Earth's climate changes in response to rising levels of human-produced greenhouse gases. Study results are published in the journal Climatic Change.
The model projections paint a portrait of increasing ecological change and stress in Earth's biosphere, with many plant and animal species facing increasing competition for survival, as well as significant species turnover, as some species invade areas occupied by other species. Most of Earth's land that is not covered by ice or desert is projected to undergo at least a 30 percent change in plant cover - changes that will require humans and animals to adapt and often relocate.
In addition to altering plant communities, the study predicts climate change will disrupt the ecological balance between interdependent and often endangered plant and animal species, reduce biodiversity and adversely affect Earth's water, energy, carbon and other element cycles.
"For more than 25 years, scientists have warned of the dangers of human-induced climate change," said Jon Bergengren, a scientist who led the study while a postdoctoral scholar at Caltech. "Our study introduces a new view of climate change, exploring the ecological implications of a few degrees of global warming. While warnings of melting glaciers, rising sea levels and other environmental changes are illustrative and important, ultimately, it's the ecological consequences that matter most."
When faced with climate change, plant species often must "migrate" over multiple generations, as they can only survive, compete and reproduce within the range of climates to which they are evolutionarily and physiologically adapted. While Earth's plants and animals have evolved to migrate in response to seasonal environmental changes and to even larger transitions, such as the end of the last ice age, they often are not equipped to keep up with the rapidity of modern climate changes that are currently taking place. Human activities, such as agriculture and urbanization, are increasingly destroying Earth's natural habitats, and frequently block plants and animals from successfully migrating.
To study the sensitivity of Earth's ecological systems to climate change, the scientists used a computer model that predicts the type of plant community that is uniquely adapted to any climate on Earth. This model was used to simulate the future state of Earth's natural vegetation in harmony with climate projections from 10 different global climate simulations. These simulations are based on the intermediate greenhouse gas scenario in the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report. That scenario assumes greenhouse gas levels will double by 2100 and then level off. The U.N. report's climate simulations predict a warmer and wetter Earth, with global temperature increases of 3.6 to 7.2 degrees Fahrenheit (2 to 4 degrees Celsius) by 2100, about the same warming that occurred following the Last Glacial Maximum almost 20,000 years ago, except about 100 times faster. Under the scenario, some regions become wetter because of enhanced evaporation, while others become drier due to changes in atmospheric circulation.
The researchers found a shift of biomes, or major ecological community types, toward Earth's poles - most dramatically in temperate grasslands and boreal forests - and toward higher elevations. Ecologically sensitive "hotspots" - areas projected to undergo the greatest degree of species turnover - that were identified by the study include regions in the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau, eastern equatorial Africa, Madagascar, the Mediterranean region, southern South America, and North America's Great Lakes and Great Plains areas. The largest areas of ecological sensitivity and biome changes predicted for this century are, not surprisingly, found in areas with the most dramatic climate change: in the Northern Hemisphere high latitudes, particularly along the northern and southern boundaries of boreal forests.
"Our study developed a simple, consistent and quantitative way to characterize the impacts of climate change on ecosystems, while assessing and comparing the implications of climate model projections," said JPL co-author Duane Waliser. "This new tool enables scientists to explore and understand interrelationships between Earth's ecosystems and climate and to identify regions projected to have the greatest degree of ecological sensitivity."
"In this study, we have developed and applied two new ecological sensitivity metrics - analogs of climate sensitivity - to investigate the potential degree of plant community changes over the next three centuries," said Bergengren. "The surprising degree of ecological sensitivity of Earth's ecosystems predicted by our research highlights the global imperative to accelerate progress toward preserving biodiversity by stabilizing Earth's climate."
Note: JPL is managed for NASA by the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
Related reading:
Ecological sensitivity: a biospheric view of climate change, Jon C. Bergengren, Duane E. Waliser and Yuk L. Yung, Journal of Climatic Change (2011) 107:433–457: DOI 10.1007/s10584-011-0065-1































 Arguments
Arguments























 0
0  0
0






Comments