At a glance - Was 1934 the hottest year on record?
Posted on 18 June 2024 by John Mason, BaerbelW, Ken Rice
On February 14, 2023 we announced our Rebuttal Update Project. This included an ask for feedback about the added "At a glance" section in the updated basic rebuttal versions. This weekly blog post series highlights this new section of one of the updated basic rebuttal versions and serves as a "bump" for our ask. This week features "Was 1934 the hottest year on record?". More will follow in the upcoming weeks. Please follow the Further Reading link at the bottom to read the full rebuttal and to join the discussion in the comment thread there.
At a glance
Let's not shy away from the fact that in the contiguous United States, the year 1934 was particularly warm. It was among a cluster of years marked by the notorious droughts known as the 'Dust Bowl' years, during which huge dust-storms were frequent and did great damage to the soils of the Prairies.
But how significant is 1934 in the bigger, global picture? Let's take a look.
The background to this tale involves the NASA GISS temperature dataset. In August 2007, blogger Steven MacIntryre noticed a series of sudden temperature leaps in that dataset. They had occurred early in the year 2000, leading some to speculate that the Y2K computer bug must have been behind them.
NASA investigated. The data used for the NASA GISS record are from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA had adjusted the data to filter out spurious excess warming. Sources of such biases are well-known. They include time of observation, non-ideal siting of weather-stations, relocation of them and urban heat island effects.
The specific error was nothing to do with Y2K. It was simply that, from January 2000, NASA were mistakenly using unadjusted data, so all those spurious anomalies were still in there and it looked warmer than it should.
Nobody's perfect and that includes scientists, but science is a self-correcting process. Errors that do occur are corrected when found. Correcting this specific error meant that some six years of temperature data had to be adjusted downwards. That meant that the order of the warmest years was also affected and after adjustment, 1934 and its Dust Bowl heat once again stood out prominently.
That's what happened back then, in a nutshell. Now to look at 1934 in context, with the added benefit of another 17 years of hindsight, of course.
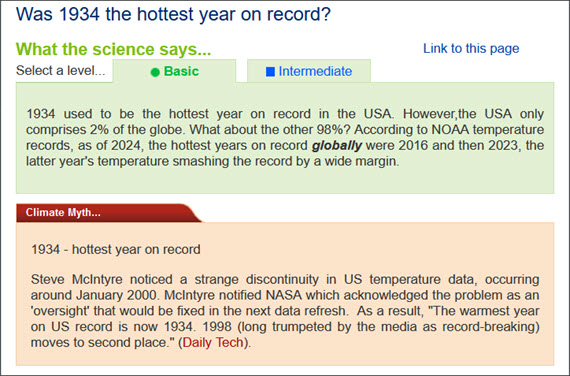
Firstly, the corrected temperature record covered only the Lower 48 - the states of the USA excluding Alaska and Hawaii - where 1934 was indeed a very hot year. Zooming out of the USA - making up around 2% of the world's surface - to the whole globe, however, shows that 1934 was in fact a rather chilly year. In order to understand what's happening to global temperatures, the whole globe - the other 98% - also needs to be considered, year in year out.
Secondly, it may have been possible to attempt crudely dressing-up 1934 as another 'final nail' in the 'global warming coffin' in 2007, but no longer. If you now look at the global league-table of warmest years, the ten hottest of them have occurred since 2010, with 2023 being just the latest record-breaker.
The year 1934 was a very warm one in the United States. No-one disputes that. In fact, it's meteorologically quite interesting. The Dust Bowl years are thought to have been at least partly human-caused - by poor agricultural land-management. But the way temperatures have gone now, 1934 is merely of local, historic importance: a curio to look back at from time to time - and a warning to look after your topsoil!
Please use this form to provide feedback about this new "At a glance" section. Read a more technical version below or dig deeper via the tabs above!
Click for Further details
In case you'd like to explore more of our recently updated rebuttals, here are the links to all of them:
If you think that projects like these rebuttal updates are a good idea, please visit our support page to contribute!































 Arguments
Arguments






























The following study published on researchgate explores the reasons why the 1930s were so hot and dry in the USA:
"Extraordinary heat during the 1930s US Dust Bowl and associated large-scale conditions. Unusually hot summer conditions occurred during the 1930s over the central United States and undoubtedly contributed to the severity of the Dust Bowl drought. We investigate local and large-scale conditions in association with the extraordinary heat and drought events, making use of novel datasets of observed climate extremes and climate reanalysis covering the past century. We show that the unprecedented summer heat during the Dust Bowl years was likely exacerbated by land-surface feedbacks associated with springtime precipitation deficits. The reanalysis results indicate that these deficits were associated with the coincidence of anomalously warm North Atlantic and Northeast Pacific surface waters and a shift in atmospheric pressure patterns leading to reduced flow of moist air into the central US. Thus, the combination of springtime ocean temperatures and atmospheric flow anomalies, leading to reduced precipitation, also holds potential for enhanced predictability of summer heat events. The results suggest that hot drought, more severe than experienced during the most recent 2011 and 2012 heat waves, is to be expected when ocean temperature anomalies like those observed in the 1930s occur in a world that has seen significant mean warming. (emphasis mine)"
www.researchgate.net/publication/275222230_Extraordinary_heat_during_the_1930s_US_Dust_Bowl_and_associated_large-scale_conditions